Desulfovibrio is a genus of gram-negative sulphate-reducing bacteria. This genus has been positively correlated to IBD, colorectal cancer (in animal model), ulcerative colitis, liver disease and autism.
Desulfovibrio spp. is predominant member of Sulfate-reducing bacteria in human gut microbiota. Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) are anaerobic microorganisms that conduct dissimilatory sulfate reduction to obtain energy, resulting in the release of a great quantity of sulfide. They are commonly isolated from environmental sources, but are also present in the digestive tract of animals and humans.
Different species of Desulfovibrio: Desulfovibrio desulfuricans, Desulfovibrio piger, Desulfovibrio fairfieldensis Desulfovibrio legallii
The bacteria produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a metabolite which can influence cell signaling and reduce oxidative stress at low concentrations and pose toxicity at higher concentrations.
References:
Chen YR, Zhou LZ, Fang ST, Long HY, Chen JY, Zhang GX. Isolation of Desulfovibrio spp. from human gut microbiota using a next-generation sequencing directed culture method. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019 Jun;68(6):553-561. doi: 10.1111/lam.13149. Epub 2019 Apr 3. PMID: 30835854. [L]
Kari E. Murros, Vy A. Huynh, Timo M. Takala and Per E. J. Saris, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 03 May 2021 Sec. Microbiome in Health and Disease, Desulfovibrio Bacteria Are Associated With Parkinson’s Disease [L]
Julien Loubinoux, Jean-Pierre Bronowicki, Ines A.C. Pereira, Jean-Louis Mougenel, Alain E. Le Faou, Sulfate-reducing bacteria in human feces and their association with inflammatory bowel diseases, FEMS Microbiology Ecology, Volume 40, Issue 2, May 2002, Pages 107–112, [L]
Vuong HE, Hsiao EY. Emerging Roles for the Gut Microbiome in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Mar 1;81(5):411-423. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.08.024. Epub 2016 Aug 26. PMID: 27773355; PMCID: PMC5285286. [L]
Fang, J., Wang, H., Zhou, Y. et al. Slimy partners: the mucus barrier and gut microbiome in ulcerative colitis. Exp Mol Med 53, 772–787 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-021-00617-8 [L]
Rowan F, Docherty NG, Murphy M, Murphy B, Calvin Coffey J, O'Connell PR. Desulfovibrio bacterial species are increased in ulcerative colitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010 Nov;53(11):1530-6. doi: 10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181f1e620. PMID: 20940602. [L]
Berry D, Reinisch W. Intestinal microbiota: a source of novel biomarkers in inflammatory bowel diseases? Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb;27(1):47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.005. PMID: 23768552. [L]
Zhu Q, Jin Z, Wu W, Gao R, Guo B, Gao Z, Yang Y, Qin H. Analysis of the intestinal lumen microbiota in an animal model of colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014 Mar 6;9(6):e90849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090849. PMID: 24603888; PMCID: PMC3946251. [L]
Xie G, Wang X, Liu P, Wei R, Chen W, Rajani C, Hernandez BY, Alegado R, Dong B, Li D, Jia W. Distinctly altered gut microbiota in the progression of liver disease. Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):19355-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8466. PMID: 27036035; PMCID: PMC4991388. [L]
Tomova A, Husarova V, Lakatosova S, Bakos J, Vlkova B, Babinska K, Ostatnikova D. Gastrointestinal microbiota in children with autism in Slovakia. Physiol Behav. 2015 Jan;138:179-87. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.10.033. Epub 2014 Nov 6. PMID: 25446201. [L]
Holscher HD, Bauer LL, Gourineni V, Pelkman CL, Fahey GC Jr, Swanson KS. Agave inulin supplementation affects the fecal microbiota of healthy adults participating in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J Nutr (2015) 145:2025–32. doi:10.3945/jn.115.217331 [L]
Vulevic J, Juric A, Tzortzis G, Gibson GR. A mixture of trans-galactooligosaccharides reduces markers of metabolic syndrome and modulates the fecal microbiota and immune function of overweight adults. J Nutr. 2013 Mar;143(3):324-31. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.166132. Epub 2013 Jan 9. PMID: 23303873. [L]
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, Peng Y, Zhang D, Jie Z, Wu W, Qin Y, Xue W, Li J, Han L, Lu D, Wu P, Dai Y, Sun X, Li Z, Tang A, Zhong S, Li X, Chen W, Xu R, Wang M, Feng Q, Gong M, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang Z, Chen H, Yang R, Zheng W, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K, Wang J. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2012 Oct 4;490(7418):55-60. doi: 10.1038/nature11450. Epub 2012 Sep 26. PMID: 23023125. [L]
Sophie Hiel, Marco A. Gianfrancesco, Julie Rodriguez, Daphnée Portheault, Quentin Leyrolle, Laure B. Bindels, Carolina Gomes da Silveira Cauduro, Maria D.G.H. Mulders, Giorgia Zamariola, Anne-Sophie Azzi, Gaetan Kalala, Barbara D. Pachikian, Camille Amadieu, Audrey M. Neyrinck, Audrey Loumaye, Patrice D. Cani, Nicolas Lanthier, Pierre Trefois, Olivier Klein, Olivier Luminet, Jérôme Bindelle, Nicolas Paquot, Miriam Cnop, Jean-Paul Thissen, Nathalie M. Delzenne,
Link between gut microbiota and health outcomes in inulin -treated obese patients: Lessons from the Food4Gut multicenter randomized placebo-controlled trial, Clinical Nutrition, Volume 39, Issue 12, 2020, Pages 3618-3628, ISSN 0261-5614, [L].
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder which is manifested through impaired social communication and repetitive behaviour, often with associated immune dysregulation and gastrointestinal disorders. Dysbiotic gut microbial profiles have been associated with ASD. Researchers have found higher abundance of Clostridia, Lactobacilli and Desulfovibrio species and decreased abundance of Bifidobacteria, Prevotella, Coprococcus and Veillonella species in subjects affected with ASD.
Ulcerative colitis (UC)
The presence of Desulfovibrio subspecies is increased in ulcerative colitis and the data presented suggest that these bacteria represent an increased percentage of the colonic microbiome in acute ulcerative colitis.
Desulfovibrio positivity was significantly increased in acute and chronic ulcerative colitis at multiple levels within the colon, and after normalization with total bacterial signal, the relative Desulfovibrio load was increased in acute colitis compared with controls. Desulfovibrio counts did not significantly correlate with age, disease duration, or disease activity but interlevel correlations were found in adjacent colonic segments in the healthy control and chronic ulcerative colitis groups.
Inflammatory bowel disease
Desulfovibrio spp. is associated with several clinical conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, but until now there are very few reports describing the isolation of Desulfovibrio spp. from human faecal samples. The implication of SRB in IBD has been suggested as their metabolic end product, hydrogen sulfide, is a cytotoxic compound. This compound may act through an inhibition of butyrate oxidation, the main energy source for colonocytes. The impairment of the functions of the intestinal epithelium would lead to cell death and chronic inflammation. However, the species of SRB associated with IBD have not yet been identified. Their identification would permit to look for virulence factors as well as their susceptibility to antimicrobial agents. The distribution of the species did not differ significantly when comparing healthy individuals and patients with non-inflammatory bowel diseases. D. piger was barely more prevalent than D. fairfieldensis. Conversely, in patients with IBD, D. piger was 4 times more frequent than D. fairfieldensis. This difference was especially noticeable for CD as IBD patients consisted mainly of CD patients. Furthermore, the prevalence of D. piger was significantly higher in patients hospitalized for IBD as compared to healthy individuals or patients hospitalized for other pathologies. There was no relation between the stage of the disease and the presence of SRB.
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
Gram-negative sulfate-reducing bacteria of the genus Desulfovibrio may play a potential role in the development of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Conventional and quantitative real-time PCR analysis of feces from twenty PD patients and twenty healthy controls revealed that all PD patients harbored Desulfovibrio bacteria in their gut microbiota and these bacteria were present at higher levels in PD patients than in healthy controls. Additionally, the concentration of Desulfovibrio species correlated with the severity of PD. Desulfovibrio bacteria produce hydrogen sulfide and lipopolysaccharide, and several strains synthesize magnetite, all of which likely induce the oligomerization and aggregation of α-synuclein protein. The substances originating from Desulfovibrio bacteria likely take part in pathogenesis of PD.
Type 2 diabetes
In a Chinese cohort, this genus, that includes sulfate-reducing bacteria, has been reported to be increased in T2DM patients.
Possible treatment options
Desulfovibrio abundance was reported to be decreased by 5.0 g of agave inulin/native inulin intake per day for 21 days. Similar findings were reported in obese subjects supplemented with a mixture of galacto-oligosaccharides.
In addition, a study in mice that were fed a diet supplemented with glycomacropeptide, a 64-amino acid glycophosphopeptide, showed that this diet reduced Desulfovibrio bacteria. This reduction was associated with decreased plasma concentrations of the inflammation markers interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, Interleukin-1beta, and Interleukin-2.
Disclaimer: Always consult your doctor or medical professional before starting any treatment plan.
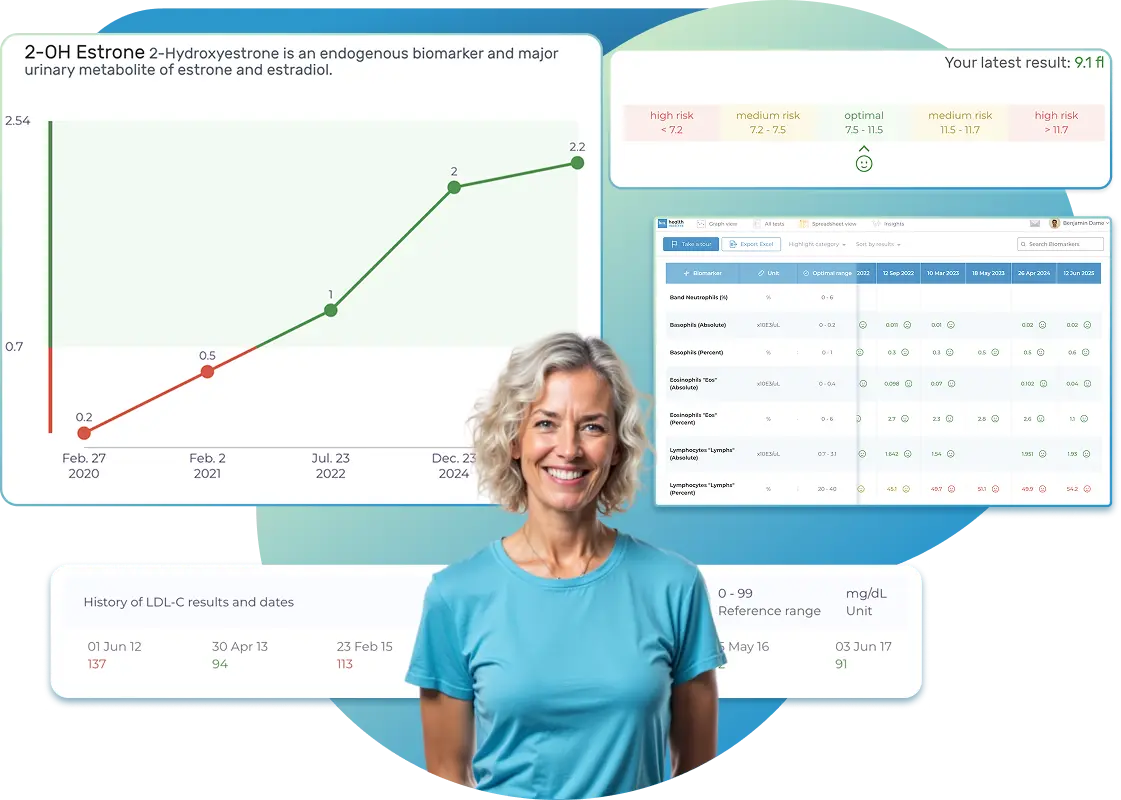
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
Laboratories
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.











Pricing Table
Choose the plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clear insights you can finally use.
Pick a plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clarity.
Personal plans
Professional plan
$15/ month
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
$250/ once
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
Professional plan
$45/ month
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
About membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
Easily upload lab results from any provider, whether it's a hospital, independent lab, or home testing service. We support PDFs, scanned documents, and JPEGs from patient portals. No need to log in to multiple platforms — everything is centralized in one secure space.
Easily upload lab results from any provider — we support PDFs, scans, and images. Keep all your reports organized in one secure place.
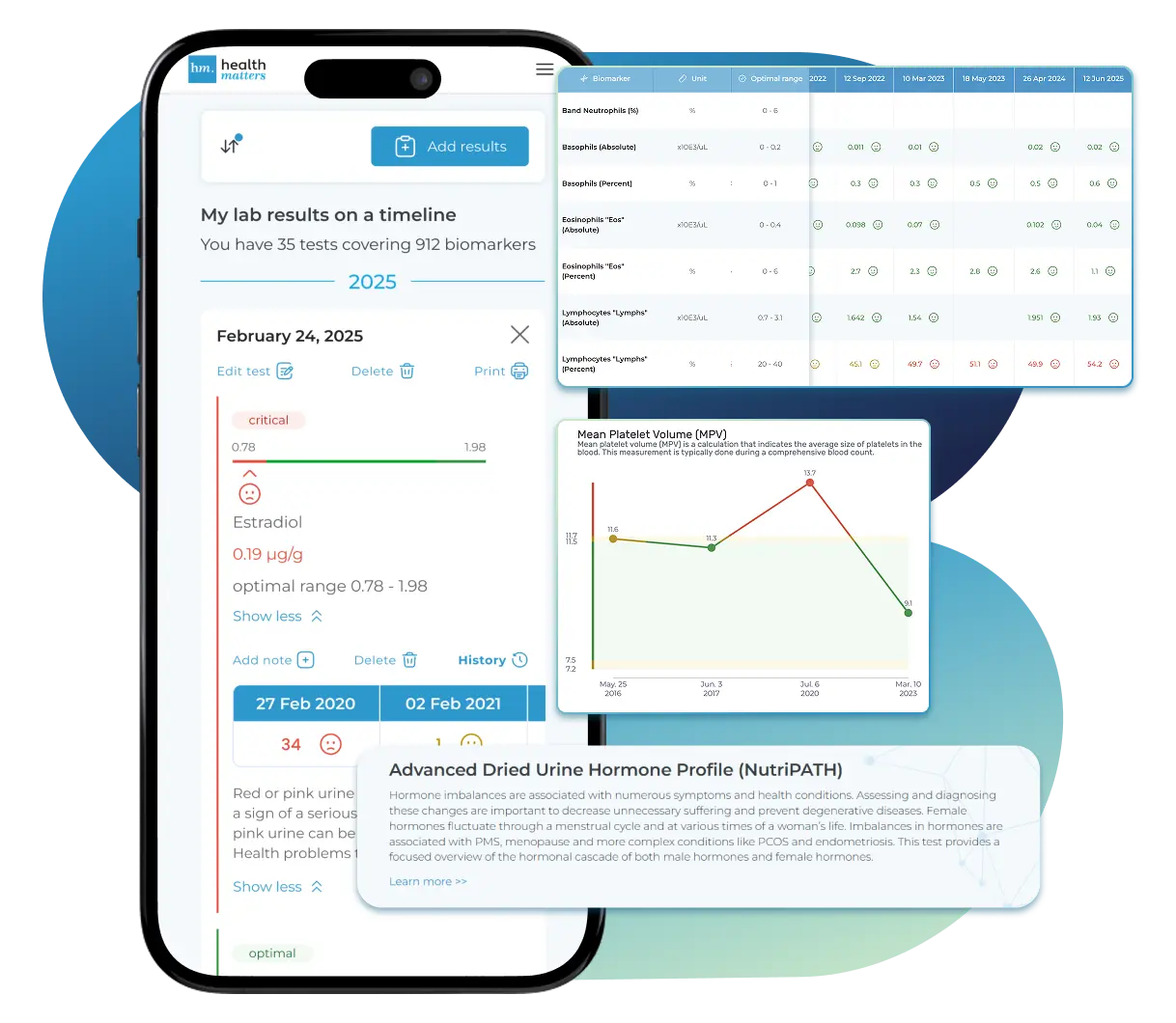
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey. Whether you're tracking a condition, managing treatments, or staying proactive, the timeline helps you and your doctor understand how things progress over time.
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey.
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
Whether it's a blood test, GI panel, urinalysis, or something else, lab reports measure numerous biomarkers that reveal what's happening inside your body. Our extensive database covers over 10,000 biomarkers, providing clear, simple explanations of what each result means and how you can take action—no matter your membership level. Say goodbye to confusion and get the insights you need to better understand your health.
Our database covers over 10,000 biomarkers with clear, simple explanations—so you can finally understand your results and what to do next.
 Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
If you'd like to handle inputting your health data into your account, you can do so with our easy-to-use data entry forms. Our user-friendly form is designed to guide you through the quick and easy submission process, making it simple to keep track of your health metrics. This is available to both Complete plan and Unlimited plan members.
Our user-friendly form guides you through a quick, simple submission process, making it easy to enter your health metrics.
Add your results anytime with our easy entry form. It's quick, guided, and helps you stay organized — free for all members.
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
View your lab data through easy-to-read graphs and tables. Quickly spot patterns, track changes, and compare results across different dates — all without digging through multiple reports. You can also select and compare graphs of specific biomarkers side-by-side to better understand how they relate and change over time.
See your lab reports in clear graphs and tables. Spot patterns, track changes, and compare results over time — all in one place.
 Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file. Choose from PDF, Excel, or CSV formats to easily review, share, or get a second opinion—no more juggling multiple reports.
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file.
 Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest. Complete plan members receive one report entered for free, then $15 per report after that. Unlimited plan members receive ten report entries for free, then $15 per report after that.
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest.
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Whether you're working with a doctor, nutritionist, caregiver, or wellness coach, you can securely share your complete lab history by sending an invite link to anyone you trust. You have full control over who sees your information and for how long, ensuring your privacy and peace of mind at every step.
Share your full lab history with your doctor, nutritionist, or coach using a secure invite link.
Discover






I have been using Healthmatters.io since 2021. I travel all over the world and use different doctors and health facilities. This site has allowed me to consolidate all my various test results over 14 years in one place. And every doctor that I show this to has been impressed. Because with any health professional I talk to, I can pull up historical results in seconds. It is invaluable. Even going back to the same doctor, they usually do not have the historical results from their facility in a graph format. That has been very helpful.
Anthony
Unlimited Plan Member since 2021

What fantastic service and great, easy-to-follow layouts! I love your website; it makes it so helpful to see patterns in my health data. It's truly a pleasure to use. I only wish the NHS was as organized and quick as Healthmatters.io. You've set a new standard for health tracking!
Karin
Advanced Plan Member since 2020

As a PRO member and medical practitioner, Healthmatters.io has been an invaluable tool for tracking my clients' data. The layout is intuitive, making it easy to monitor trends and spot patterns over time. The ability to customize reports and charts helps me present information clearly to my clients, improving communication and outcomes. It's streamlined my workflow, saving me time and providing insights at a glance. Highly recommended for any practitioner looking for a comprehensive and user-friendly solution to track patient labs!
Paul
Healthmatters Pro Member since 2024
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 4000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
While we work with many popular labs, we welcome reports from lots of other places too.
It's as simple as this: if you can get a test done, you can upload it to Healthmatters and we can interpret results from any lab out there. If laboratories can analyze it, we can interpret it.
If you're on the hunt for a specific biomarker, contact us and we'll add it to our database. Anything from blood, urine, saliva, or stool can be uploaded, understood, and tracked with your Healthmatters account.
The Complete Plan ($15/month) is perfect for individuals who want ongoing access to their health data. It includes unlimited lab imports, visual tracking, custom ranges, result explanations, full account exports, and secure sharing — all with a simple monthly subscription. You can cancel anytime and restart your plan whenever you're ready — your data will still be there waiting for you. You can also upgrade to the Unlimited Plan at any time, with the cost prorated based on what you've already paid.
The Unlimited Plan ($250 one-time) is also designed for individuals but offers lifetime access with no ongoing subscription. You'll get all the same features as the Complete Plan, plus a larger initial data entry allowance (10 reports), making it a great choice if you prefer a one-time payment and long-term use without monthly fees.
In short:
There are two ways to add your test reports to your Healthmatters account. One option is to input the data using the data entry forms. The other method is to utilize our "Data entry service."
Our data entry forms offer an easy, fast, and free way for you to input the reports yourself. Self-entry allows you to add an unlimited number of reports at no cost. We make the self-entry process user-friendly, providing dozens of templates that pre-populate the most popular laboratory panels and offering instant feedback on entered values.
For those who prefer assistance, we offer a "Data entry service" to help you input your data. Simply attach an image or file of your lab test results, and a qualified team member from our data entry team will add the results for you.
We support various file types, including PDFs, JPGs, or Excel. This service is particularly useful if you have many reports to upload or if you're too busy to handle the data entry yourself.
Our Data Entry Service is for when you don't want to manually type in your lab results yourself. You simply upload your report (PDF, image, or screenshot), and our trained team enters the information into your Healthmatters account for you — accurately and neatly organized, ready to view in graphs, tables, and timelines.
The $15 per report covers the time and care it takes for a real person to review your file, make sure each result is entered correctly, and double-check for accuracy. This ensures your health data is precise and easy to work with — without you having to spend the time doing it yourself.
Prefer to do it yourself? You can always use our free self-entry tool to add results manually — it just takes a bit more time and attention.
For users on the Complete monthly plan, the first report is entered free of charge, and each additional report incurs a fee of $15.
Unlimited account holders enjoy the entry of ten reports without charge. Subsequent reports are subject to a $15 fee per report.
Additionally, users on the Complete plan can upgrade to a yearly subscription from the account settings. The annual subscription includes a data entry service for five reports.
All professional accounts allow you to import and onboard an unlimited number of clients and their lab results. The distinction between professional plans lies solely in the data entry service.
The Pro Monthly Plus plan is priced at $75 per month and includes a data entry service for five reports each month. Additional reports can be self-entered at no extra cost or, if preferred, you can use our data entry service for an additional fee of $15 per report.
The Pro Monthly plan is priced at $45 per month and does not include a data entry service. Self-entry is free for an unlimited number of reports, and you can opt for the data entry service at a fee of $15 per report.
You also have the option to upgrade to higher monthly or to annual plans, which come with substantial discounts. All upgrades can be done directly from your account.
Simply log in and navigate to your account settings to cancel your subscription. Scroll down to locate the 'Cancel' button at the bottom of the page. Ensure you cancel at least one day before the renewal date to prevent any charges. Once cancellation is requested, the subscription remains active until the conclusion of the current billing cycle.
Our goal has been to make your Healthmatters account as intuitive as possible.
We've crafted multiple ways for you to navigate your data, whether you're glancing at a single report or delving into your historical test reports.
1. Graph View:Dive into a visual journey with our biomarker graphs, showcasing over 40 data points. Combining years of results unveils trends, empowering you to make informed decisions. Our visualization tools make it a breeze to compare and understand changes over time, even if your results are from different labs. A search function and filters simplify the exploration of extensive data, allowing you to focus on what needs attention.
2. All Tests ViewExplore neatly organized reports on a timeline, highlighting crucial details like dates, critical results, and lab/panel names. Each report opens up to reveal in-depth descriptions and additional recommendations for each biomarker. The history of previous results is just a click away, and you can download a comprehensive report for deeper insights. Color-coded and user-friendly, it's designed for easy reading, understanding, and navigation.
3. Table View:For a holistic view of all biomarkers side by side, our table view is your go-to. Results are neatly displayed in a categorized and dated table, ideal for those with an extensive test history. Utilize sorting, filters, and color-coding to enhance your analysis and gain extra insights.
Yes, you can download your information anytime. We offer two easy ways to export your lab data:
This makes it simple to save, back up, or share your health data whenever you need.
Yes, you can print your report. To do so, navigate to "All tests" and open the report you wish to print. You'll find a print button in the right corner of the report. Click on it, and your browser's print window will open. If you prefer to print in a bigger typeface, adjust the scale using the print window settings.
Yes, you can! We highly recommend activating Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for your account. To do so, please navigate to the "Profile and Security" section of your account, where you will find instructions for activating 2FA.
Yes, you can. When entering values for the biomarker, you will see an "Edit Range" button. Click this button, and you'll have the option to enter a custom range.
A personal account is all about keeping your own lab test results in check. It's just for you and your personal use.
The professional account is designed for health professionals who wish to track and organize their clients' laboratory results.
To learn more about Healthmatters Pro, please refer to the professional page.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.

