Hemoglobin A2 (Quant), a key parameter in the Thalassemia and Hemoglobinopathy Comprehensive (COMP) panel, is pivotal in diagnosing and managing various blood disorders. This comprehensive panel is designed to detect and monitor conditions involving abnormal hemoglobin, like thalassemia and hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobin A2, which consists of two alpha and two delta globin chains, normally comprises a small fraction of the total hemoglobin in adults. The quantitative assessment of Hemoglobin A2 is essential, as its elevated levels are a hallmark feature in beta-thalassemia and other related hemoglobinopathies. In beta-thalassemia, there is a reduced or absent production of beta globin chains, leading to a compensatory increase in Hemoglobin A2. Therefore, a detailed measurement of Hemoglobin A2 is crucial for the accurate diagnosis of beta-thalassemia, aiding in differentiating it from other types of thalassemia and hemoglobinopathies. The precision of the Hemoglobin A2 (Quant) test within the COMP panel is instrumental in guiding clinicians in the development of targeted treatment and management plans for patients with these conditions. This test exemplifies the significant advancements in medical diagnostics, underscoring its vital role in improving patient outcomes through early detection and effective management of genetic blood disorders.
What does it mean if your Hemoglobin A2 (Quant) result is too high?
Elevated levels of Hemoglobin A2 (HbA2) in a blood test can indicate certain health conditions, most notably beta thalassemia, a blood disorder. Hemoglobin is a protein in your red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout your body. There are several types of hemoglobin, and Hemoglobin A2 is one of them, though it makes up a small fraction of the total hemoglobin in healthy individuals.
What Does It Mean?
An increase in HbA2 levels generally means that there's a higher proportion of this type of hemoglobin than what's typically expected. Normally, HbA2 comprises about 2-3% of total hemoglobin. Elevated levels are those exceeding 3.5%. Such an increase is often a hallmark sign of beta thalassemia, particularly the beta thalassemia trait (carrier state) or beta thalassemia minor, a less severe form of the disease. It's important to note that elevated HbA2 by itself doesn't cause symptoms or require treatment but serves as an indicator of underlying genetic conditions affecting hemoglobin production.
Causes:
The primary cause of elevated HbA2 levels is beta thalassemia, a genetic disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin. This condition is inherited, meaning it's passed down from parents to their children through genes. There are other less common causes for elevated HbA2, including some forms of anemia and other genetic hemoglobin variants, but these are much rarer.
Symptoms:
The symptoms are not directly caused by the elevated HbA2 itself but by the underlying condition, such as beta thalassemia. In beta thalassemia minor, symptoms might be absent or very mild and can include fatigue, weakness, or a pale appearance due to anemia (a lower than normal number of red blood cells). In more severe forms of beta thalassemia, symptoms can be more pronounced, including severe anemia, growth delays in children, bone abnormalities, and more.
Potential Treatment Options:
Treatment depends on the underlying condition causing the elevation of HbA2. For beta thalassemia minor, often no treatment is required other than perhaps monitoring and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. For more severe thalassemia conditions, treatment options can include regular blood transfusions to maintain healthy hemoglobin levels and iron chelation therapy to remove excess iron from the body (a side effect of frequent transfusions). In some cases, a bone marrow or stem cell transplant may be considered, especially in younger, severely affected individuals.
Directly lowering HbA2 levels is not the goal of treatment; rather, the focus is on managing the symptoms and complications of the underlying condition, such as beta thalassemia. For carriers or those with mild forms, regular health check-ups to monitor their condition may be all that's needed. For individuals with more severe forms, a comprehensive treatment plan developed by a healthcare provider specializing in blood disorders will be necessary. This plan may include lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, and possibly medical interventions as mentioned above.
In summary, elevated Hemoglobin A2 levels signal a need for further investigation to determine the underlying cause, usually a form of thalassemia. Understanding the genetic and familial aspect of these conditions is crucial for management and treatment planning. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a personalized approach based on the specific diagnosis and health status.
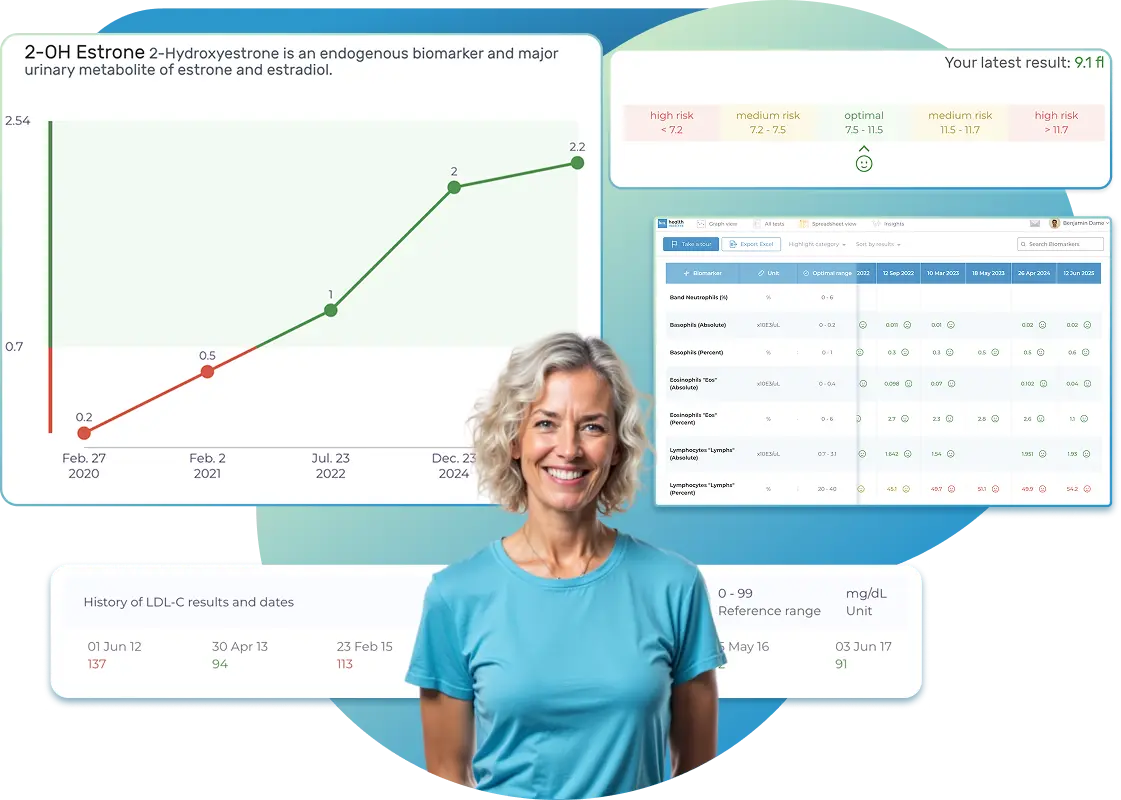
All Your Lab Results.
One Simple Dashboard.
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results Easily
Import, Track, and Share Your Lab Results
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
What does it mean if your Hemoglobin A2 (Quant) result is too low?
Low levels of Hemoglobin A2 (HbA2) refer to a decrease in the amount of a specific type of hemoglobin that is found in the red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. It is composed of several types, including Hemoglobin A, Hemoglobin A2, and Hemoglobin F. Hemoglobin A2 makes up about 2-3% of the total hemoglobin in adults. It consists of two alpha and two delta chains, differing from the most common type, Hemoglobin A, which has two alpha and two beta chains.
A decrease in Hemoglobin A2 levels is less commonly discussed than an increase, as elevated HbA2 levels are a hallmark for the diagnosis of beta-thalassemia, a blood disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin. However, low levels of HbA2, though not commonly highlighted, can still be significant in the context of diagnosing other blood-related conditions or issues.
The causes of low Hemoglobin A2 levels are not typically focused on specific diseases but can be related to a variety of conditions affecting hemoglobin production or the proportion of its different types. For example, alpha-thalassemia, a condition where there is a defect in one or more of the alpha globin genes, can lead to abnormal hemoglobin production, affecting the overall hemoglobin makeup, including HbA2 levels. It's also possible that genetic factors or other hemoglobinopathies (disorders affecting the structure or production of hemoglobin) might contribute to lower HbA2 levels.
Symptoms associated with low HbA2 levels would generally be tied to the underlying condition affecting the hemoglobin. Since HbA2 itself is a minor component of total hemoglobin, low levels might not directly lead to symptoms unless associated with a broader hemoglobinopathy or blood disorder. In cases where an underlying condition causes reduced overall hemoglobin production or function, symptoms might include fatigue, weakness, pallor (pale skin), shortness of breath, and anemia.
Treatment options for low HbA2 levels are focused on addressing the underlying cause. If the low level of HbA2 is due to a condition like alpha-thalassemia, treatment might involve regular monitoring, dietary supplements (like iron, folic acid, or vitamin B12, depending on the patient's specific needs and deficiencies), and sometimes blood transfusions in more severe cases. Genetic counseling might also be recommended for individuals with hereditary conditions affecting hemoglobin.
To address low levels of HbA2 specifically, it's crucial first to identify the underlying issue through comprehensive blood tests and possibly genetic testing. Once the cause is identified, a healthcare provider can recommend a treatment plan. In many cases, managing low HbA2 levels involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, dietary supplements, and regular medical monitoring to manage any associated conditions and maintain overall health.
In summary, while low levels of Hemoglobin A2 are less commonly a focus of medical concern compared to high levels, they can still indicate underlying issues with blood health. Identifying and treating any underlying conditions is key to managing low HbA2 levels and ensuring healthy hemoglobin function overall.
Laboratories
Bring All Your Lab Results Together — In One Place
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.
Pricing Table
Gather Your Lab History — and Finally Make Sense of It
Finally, Your Lab Results Organized and Clear
Personal plans
$79/ year
Advanced Plan
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 5 reports entered for you
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
$250/ once
Unlimited Account
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track all results with visual tools
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export your full lab history anytime
- Share results securely with anyone
- Receive 10 reports entered for you
- No subscriptions. No extra fees.
$45/ month
Pro Monthly
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
- Import lab results from any provider
- Track lab results for multiple clients
- Customize reference ranges per client
- Export lab histories and reports
- Begin with first report entered by us
- Cancel or upgrade anytime
About membership
What's included in a Healthmatters membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
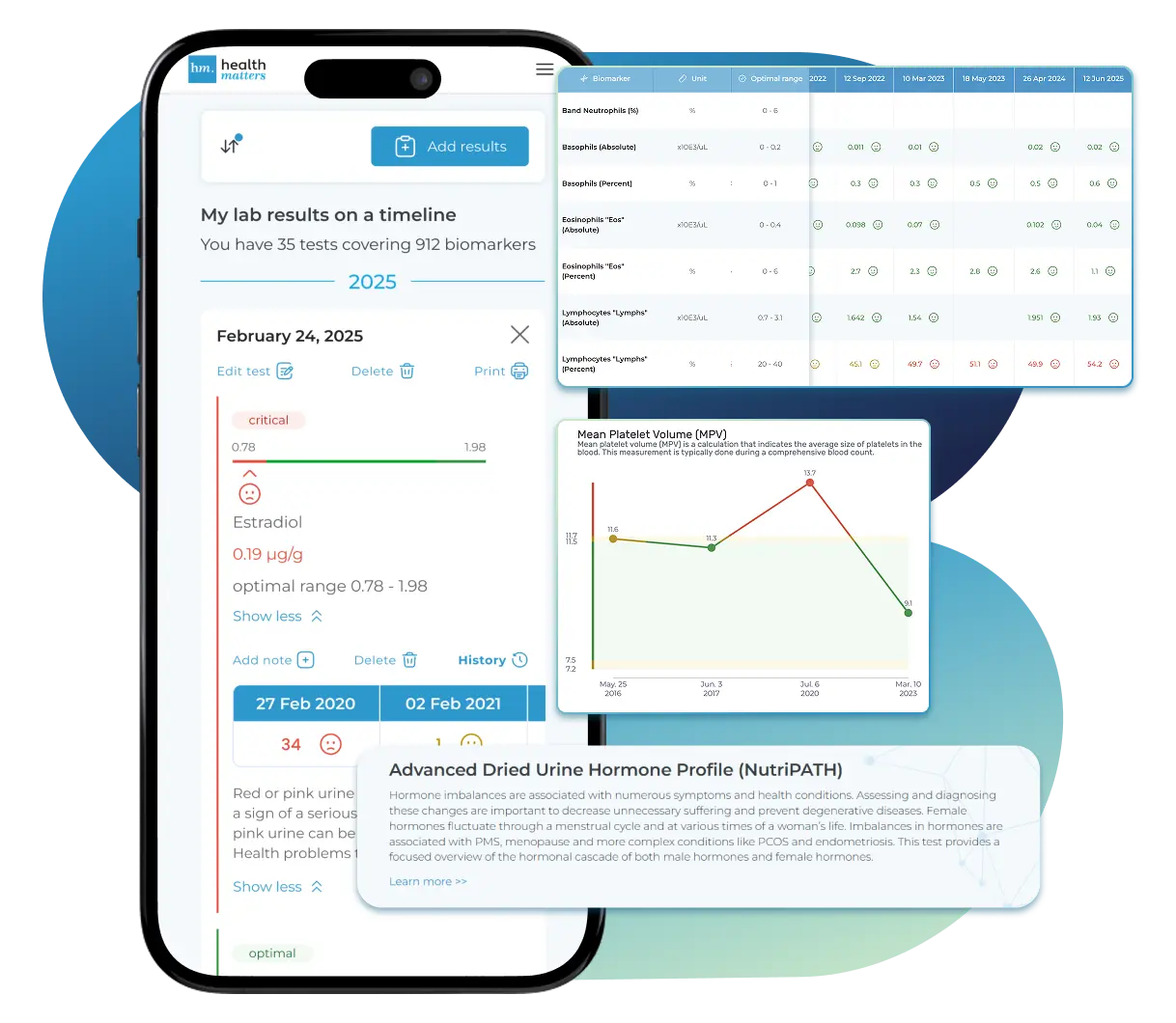
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
 Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Let Your Lab Results Tell the Full Story
Once your results are in one place, see the bigger picture — track trends over time, compare data side by side, export your full history, and share securely with anyone you trust.





Bring all your results together to compare, track progress, export your history, and share securely.
What Healthmatters Members Are Saying
Frequently asked questions
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
- Individuals who want to track and understand their health over time.
- Health professionals, such as doctors, nutritionists, and wellness coaches, need to manage and interpret lab data for their clients.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
- Upload lab reports from any lab
- View your data in interactive graphs, tables, and timelines
- Track trends and monitor changes over time
- Customize your reference ranges
- Export and share your full lab history
- Access your results anytime, from any device
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 10000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
- The GI Effects® Comprehensive Stool Profile,
- GI-MAP,
- The NutrEval FMV®,
- The ION Profile,
- Amino Acids Profile,
- Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH),
- Organic Acids Test,
- Organix Comprehensive Profile,
- Toxic Metals,
- Complete Blood Count (CBC),
- Metabolic panel,
- Thyroid panel,
- Lipid Panel,
- Urinalysis,
- And many, many more.
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
We implement proven measures to keep your data safe.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
















