Mucosal surfaces, such as those of the eyes, nose, throat, and GI tract, represent a large port of entry for pathogens and thus must be efficiently protected.
This goal is achieved by a combination of innate and acquired immunoactivity. Innate immunity includes mucus, lactoferrin, lysozymes, and certain cytokines. Acquired immunity includes the production of antibodies.
The primary antibody response at the mucosal level is secretory IgA (sIgA). sIgA is produced by activated B-cells in the mucosa where it forms immune complexes with pathogens and allergens, thereby preventing them from binding to and penetrating the intestinal mucosa. IgG is also found in the mucosa, but they are believed to be serum derived.
Antibody deficiencies are the most commonly reported immunodeficiencies worldwide.
Selective IgA deficiency is the most common primary immunodeficiency, with prevalence from as low as 1 in 223 in community studies to 1 in 400 in healthy blood donors. Diagnosis is made with a serum IgA, though salivary and fecal sIgA levels are also found to be absent or low. Patients can also have a partial IgA deficiency, which isn’t a genetic immunodeficiency. Rather, a partial IgA deficiency may be caused by environmental or lifestyle factors, such as nutrient deficiencies, drugs, virus’, or impaired immune function, that can lead to chronic IgA stimulation.
Over time, IgA production may decrease and a deficiency may be noticed in fecal, saliva or serum total IgA levels. Patients with low IgA levels have increased risk of infections in mucosal surfaces, food allergies, celiac- like enteropathies, IBD, and autoimmune disorders.
Some patients also have gastrointestinal issues and chronic diarrhea. Since sIgA serves to protect the gut, lower levels can also lead to an increased risk of leaky gut or dysbiosis.
Leaky gut syndrome is your first line of defense, sIgA is decreased and is unable to adequately fight invaders trying to get into the intestinal epithelium. When the epithelium becomes inflamed and irritated, the tight junctions in the epithelium become weakened and allow toxins or antigens, generally food particles, to enter.
These entering food particles cause the body to react by creating other classes of immunoglobulins, primarily IgG, to protect the blood and tissues. A patient with leaky gut may therefore have IgG reactions to many foods. An IgA deficiency can also lead to false-negative IgA-based test results, such as celiac.
IgA deficiencies occurred in 1 out of 131 patients tested for celiac disease. Many patients with IgA deficiency are asymptomatic. It is not understood why some individuals with IgA deficiency have almost no illness while others are very sick. Studies have suggested that some patients may be missing a fraction of their IgG (the IgG2 and/or IgG4 subclasses), and that may be part of the explanation of why some patients with IgA deficiency are more susceptible to infection than others. Also, it is not known precisely what percent of individuals with IgA deficiency will eventually develop complications; estimates range from 25% to 50% over 20 years of observation. The clinical manifestation in a given patient tends to remain constant (e.g. in patients with autoimmune conditions, recurrent infections do not tend to develop).
Clinical applications of secretory IgA antibody testing:
- Production is stimulated by bacteria & viruses, which are removed by sIgA and phagocytosis
- Patients deficient in sIgA are susceptible to pathogens in the G.I tract
- There is a particularly high prevalence of IgA deficiency in coeliacs (5%)
- Deficiencies may be associated with asthma, autoimmune disease, candidiasis, coeliac disease and food allergies
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s patients all have low sIgA. There is some evidence that increasing the levels may help disease
- High levels are often found in patients with chronic infection (CMV, EBV and HIV)
- Lifestyle and nutritional factors influence levels
- Choline, EFA’s, glutathione, glycine, phosphatidylcholine, Vitamin C & zinc are all needed for efficient production
- Chronic dermatological conditions
Elevated levels in saliva are associated with an immune response to stimulation by infections and inflammatory reactions. High levels of SIgA production may indicate an infection of the digestive system, in which case a Comprehensive Stool Analysis with parasites would be recommended.
Causes of elevated fecal sIgA:
- Any defective epithelial barrier
- A defective epithelial barrier allows bacterial and microbial penetration, which is the strongest stimulator of sIgA production.
- Celiac disease
- Colon cancer
- Infections
- IBS (especially the diarrhea subtype)
Therapeutic considerations for elevated fecal sIgA:
Assess for and treat root causes of immune upregulation /inflammation:
- Infection (bacterial, parasitic, and/or viral pathogen, potential pathogen)
- Compromised intestinal barrier function (i.e., intestinal permeability)
- Heightened response to noninfectious stimuli (i.e., food sensitivity/allergy, etc.)
Consider Food Antibody testing – If positive, consider elimination diet
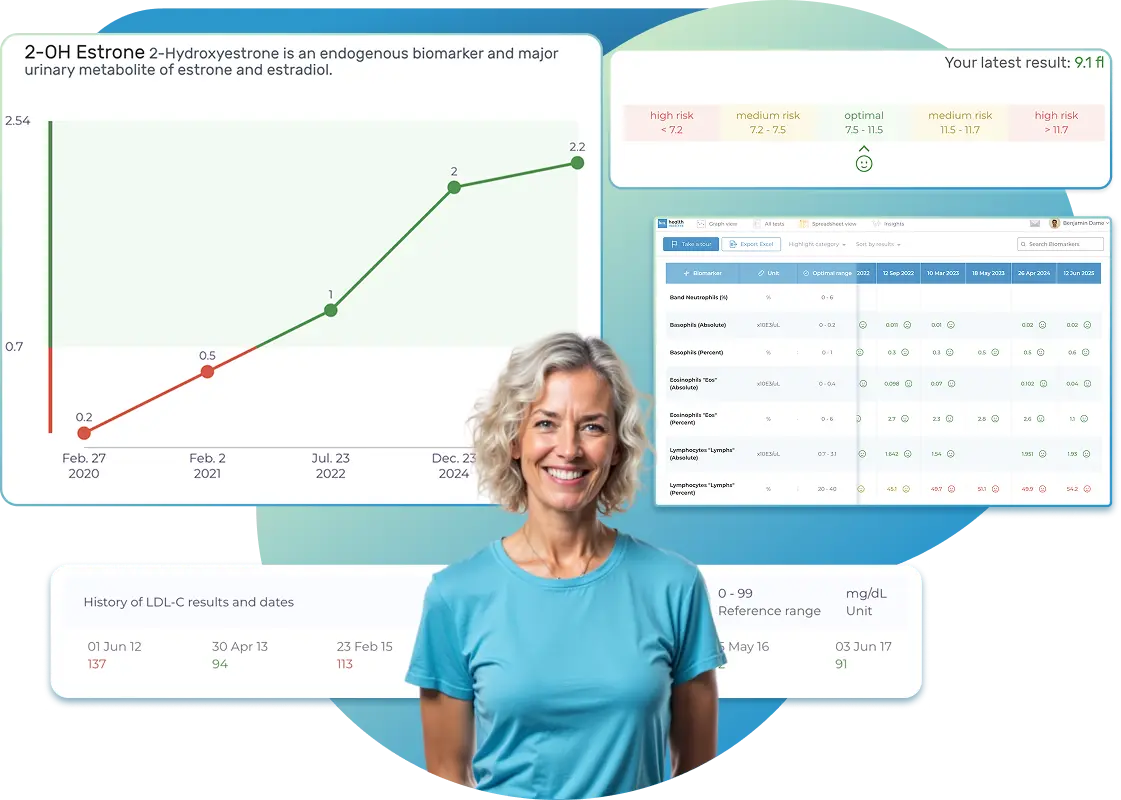
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
SIgA key function is to bind to invading micro organisms and toxins and entrap them in the mucus layer or within the epithelial cells [=cells that cover the inside and outside of the surfaces of your body], so inhibiting microbial motility, agglutinating the organisms and neutralising their exotoxins and then assist in their harmless elimination from the body in the faecal flow.
SIgA also 'tags' food as acceptable, so low SIgA leads to increased sensitivity to foods. Several studies link stress and emotionality with levels of SIgA.
Production is adversely affected by stress, which is mediated by cortisol levels. This could result in inadequate production of SIgA in response to a mucosal infection. Reduced SIgA levels may be associated with sub optimal adrenal output, in which case an adrenal stress index test would be recommended.
Causes of Low sIgA:
- Certain drugs can induce transient IgA deficiency which resolve after the causative drugs are removed. These include anti-inflammatories, sulfasalazine, hydantoin, cyclosporine, gold, fenclofenac, sodium valproate, and captopril.
- Certain viral infections, such as congenital rubella infection or Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, may result in persistent IgA deficiency.
- Patients with poor nutrition may have difficulty mounting an appropriate immune response.
- Lower sIgA levels are frequently found in those with ulcerative colitis or in those whose first degree relatives have the disease. Research has shown a dysfunction in transepithelial IgA secretion, and thus a decrease in sIgA.
- A high antigenic load can result in depressed sIgA, even in healthy, asymptomatic individuals.
- Lower levels are found in those with excessive cortisol production, so decreasing stress may lead to higher sIgA levels.
- Lower levels may also be found in those with chronic infections or immune hypersensitivity. The decrease in resistance can lead to dysbiosis and an increased risk of infection and allergy.
Considerations for low fecal sIgA:
Because of the lack of clinical evidence, there is no clear cut-off value for low fecal sIgA. People with systemic IgA deficiency can have low levels of fecal secretory IgA. There is a demonstrated link between IgA deficiency and several GI diseases, including:
- celiac disease,
- giardiasis,
- nodular lymphoid hyperplasia,
- ulcerative colitis,
- Crohn’s disease,
- pernicious anemia,
- and gastric and colonic adenocarcinoma.
Low sIgA may reflect a loss of GI immune response resiliency. Fecal sIgA may be low in severe/prolonged IBD patients due to a switch from intestinal IgA to IgG production as well as a deficiency in producing IgA dimers and polymers.
Secretory IgA demonstrates an array of activities integral to the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. It influences the composition of intestinal microbiota, down-regulates pro-inflammatory responses normally associated with the uptake of highly pathogenic bacteria and potentially allergenic antigens, and promotes the retro-transport of antigens across the intestinal epithelium to gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Therefore, a low sIgA is clinically significant.
The test result should be considered together with any other medical condition, other biomarkers, and microbiome profiles when interpreting the data.
Ways to Increase sIgA:
Treating the overall gut, with exclusion or rotation diets, glutamine, fish oils for inflammation, and the entire 4-R program includes:
Treatment Using Four “R” Program for Intestinal Health:
- Remove offending foods, medications, gluten (if sensitive) and reduce high fat foods, refined carbohydrates, sugars, and fermented foods (if yeast is present). Consider antimicrobial, antifungal, and/ or antiparasitic therapies in the case of opportunistic/ pathogenic bacterial, yeast, and/or parasite overgrowth (see otherrecommendations below).
- Replace what is needed for normal digestion and absorption such as betaine HCl, pancreatic enzymes, herbs that aid in digestion such as deglycyrrhizinated licorice and marshmallow root, dietary fiber, and water.
- Reinoculate with favorable microbes (probiotics such as Lactobacillus sp., Bifidobacter sp., and Saccharomyces boulardii). To enhance the growth of the favorable bacteria, supplement with prebiotics such as insulin, xylooligosaccharides, and fiber.
- Repair mucosal lining by giving support to healthy intestinal mucosal cells, goblet cells, and to the immune system. Consider L-glutamine, essential fatty acids, zinc, pantothenic acid and vitamin C.
Other Recommendations for Increasing sIgA:
- Exercise and relaxation techniques (such as footbaths, aromatherapy and massage) have been shown to increase sIgA levels.
- Decrease cortisol levels. Cortisol can direct the production of immune cells immuncytes, which produce sIgA.
- Probiotics (bifidobacter and Lactobacillus bacteria) have been shown to increase sIgA (as well as beneficial short chain fatty acids). They may also activate macrophages.
- Saccharomyces boulardii is used for the prevention and treatment of diarrhea of different etiologies and has been shown to enhance IgA immune response.
Laboratories
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.











Pricing Table
Choose the plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clear insights you can finally use.
Pick a plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clarity.
Personal plans
Professional plan
$15/ month
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
$250/ once
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
Professional plan
$45/ month
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
About membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
Easily upload lab results from any provider, whether it's a hospital, independent lab, or home testing service. We support PDFs, scanned documents, and JPEGs from patient portals. No need to log in to multiple platforms — everything is centralized in one secure space.
Easily upload lab results from any provider — we support PDFs, scans, and images. Keep all your reports organized in one secure place.
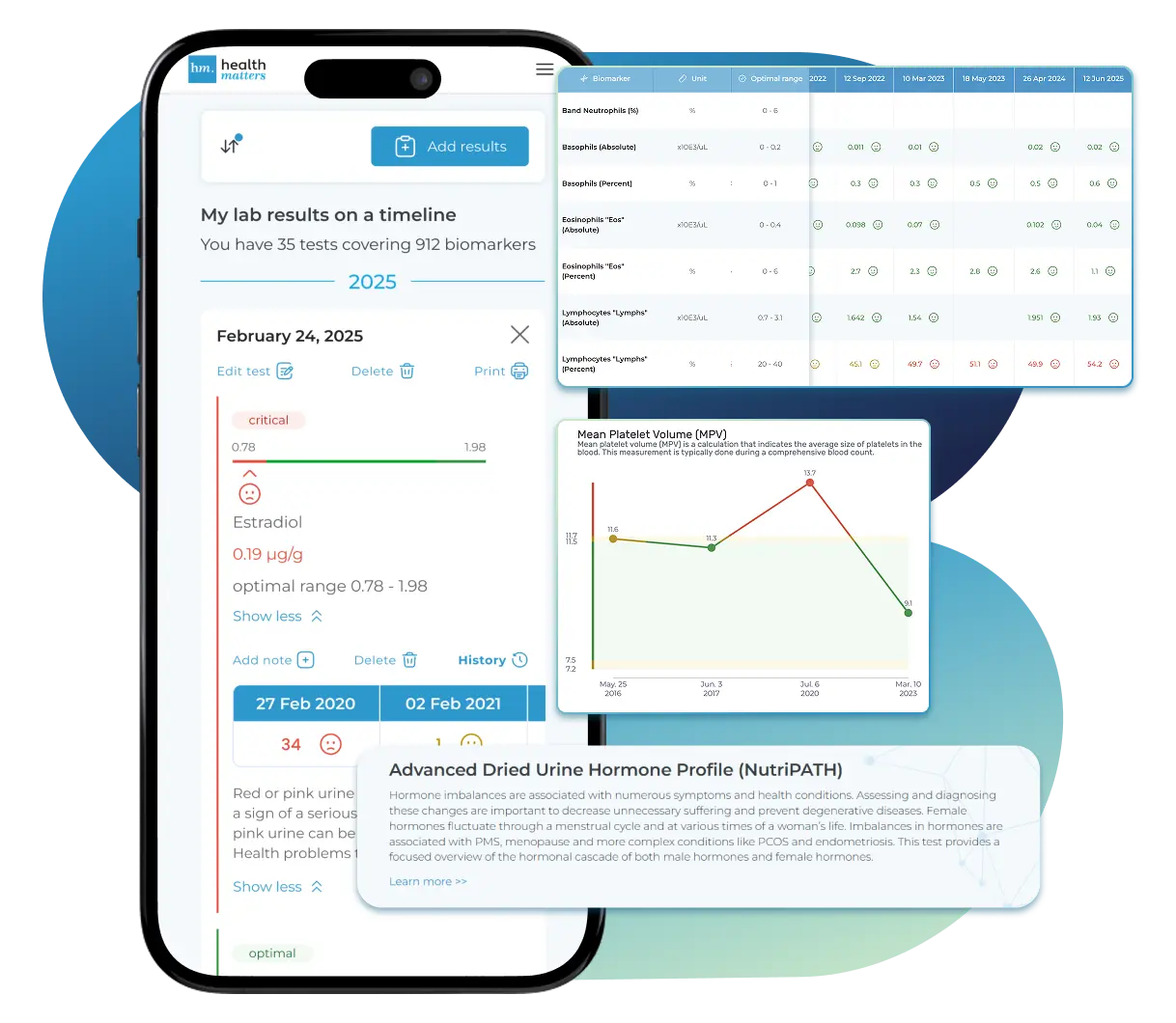
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey. Whether you're tracking a condition, managing treatments, or staying proactive, the timeline helps you and your doctor understand how things progress over time.
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey.
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
Whether it's a blood test, GI panel, urinalysis, or something else, lab reports measure numerous biomarkers that reveal what's happening inside your body. Our extensive database covers over 10,000 biomarkers, providing clear, simple explanations of what each result means and how you can take action—no matter your membership level. Say goodbye to confusion and get the insights you need to better understand your health.
Our database covers over 10,000 biomarkers with clear, simple explanations—so you can finally understand your results and what to do next.
 Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
If you'd like to handle inputting your health data into your account, you can do so with our easy-to-use data entry forms. Our user-friendly form is designed to guide you through the quick and easy submission process, making it simple to keep track of your health metrics. This is available to both Complete plan and Unlimited plan members.
Our user-friendly form guides you through a quick, simple submission process, making it easy to enter your health metrics.
Add your results anytime with our easy entry form. It's quick, guided, and helps you stay organized — free for all members.
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
View your lab data through easy-to-read graphs and tables. Quickly spot patterns, track changes, and compare results across different dates — all without digging through multiple reports. You can also select and compare graphs of specific biomarkers side-by-side to better understand how they relate and change over time.
See your lab reports in clear graphs and tables. Spot patterns, track changes, and compare results over time — all in one place.
 Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file. Choose from PDF, Excel, or CSV formats to easily review, share, or get a second opinion—no more juggling multiple reports.
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file.
 Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest. Complete plan members receive one report entered for free, then $15 per report after that. Unlimited plan members receive ten report entries for free, then $15 per report after that.
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest.
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Whether you're working with a doctor, nutritionist, caregiver, or wellness coach, you can securely share your complete lab history by sending an invite link to anyone you trust. You have full control over who sees your information and for how long, ensuring your privacy and peace of mind at every step.
Share your full lab history with your doctor, nutritionist, or coach using a secure invite link.
Discover






I have been using Healthmatters.io since 2021. I travel all over the world and use different doctors and health facilities. This site has allowed me to consolidate all my various test results over 14 years in one place. And every doctor that I show this to has been impressed. Because with any health professional I talk to, I can pull up historical results in seconds. It is invaluable. Even going back to the same doctor, they usually do not have the historical results from their facility in a graph format. That has been very helpful.
Anthony
Unlimited Plan Member since 2021

What fantastic service and great, easy-to-follow layouts! I love your website; it makes it so helpful to see patterns in my health data. It's truly a pleasure to use. I only wish the NHS was as organized and quick as Healthmatters.io. You've set a new standard for health tracking!
Karin
Advanced Plan Member since 2020

As a PRO member and medical practitioner, Healthmatters.io has been an invaluable tool for tracking my clients' data. The layout is intuitive, making it easy to monitor trends and spot patterns over time. The ability to customize reports and charts helps me present information clearly to my clients, improving communication and outcomes. It's streamlined my workflow, saving me time and providing insights at a glance. Highly recommended for any practitioner looking for a comprehensive and user-friendly solution to track patient labs!
Paul
Healthmatters Pro Member since 2024
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 4000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
While we work with many popular labs, we welcome reports from lots of other places too.
It's as simple as this: if you can get a test done, you can upload it to Healthmatters and we can interpret results from any lab out there. If laboratories can analyze it, we can interpret it.
If you're on the hunt for a specific biomarker, contact us and we'll add it to our database. Anything from blood, urine, saliva, or stool can be uploaded, understood, and tracked with your Healthmatters account.
The Complete Plan ($15/month) is perfect for individuals who want ongoing access to their health data. It includes unlimited lab imports, visual tracking, custom ranges, result explanations, full account exports, and secure sharing — all with a simple monthly subscription. You can cancel anytime and restart your plan whenever you're ready — your data will still be there waiting for you. You can also upgrade to the Unlimited Plan at any time, with the cost prorated based on what you've already paid.
The Unlimited Plan ($250 one-time) is also designed for individuals but offers lifetime access with no ongoing subscription. You'll get all the same features as the Complete Plan, plus a larger initial data entry allowance (10 reports), making it a great choice if you prefer a one-time payment and long-term use without monthly fees.
In short:
There are two ways to add your test reports to your Healthmatters account. One option is to input the data using the data entry forms. The other method is to utilize our "Data entry service."
Our data entry forms offer an easy, fast, and free way for you to input the reports yourself. Self-entry allows you to add an unlimited number of reports at no cost. We make the self-entry process user-friendly, providing dozens of templates that pre-populate the most popular laboratory panels and offering instant feedback on entered values.
For those who prefer assistance, we offer a "Data entry service" to help you input your data. Simply attach an image or file of your lab test results, and a qualified team member from our data entry team will add the results for you.
We support various file types, including PDFs, JPGs, or Excel. This service is particularly useful if you have many reports to upload or if you're too busy to handle the data entry yourself.
Our Data Entry Service is for when you don't want to manually type in your lab results yourself. You simply upload your report (PDF, image, or screenshot), and our trained team enters the information into your Healthmatters account for you — accurately and neatly organized, ready to view in graphs, tables, and timelines.
The $15 per report covers the time and care it takes for a real person to review your file, make sure each result is entered correctly, and double-check for accuracy. This ensures your health data is precise and easy to work with — without you having to spend the time doing it yourself.
Prefer to do it yourself? You can always use our free self-entry tool to add results manually — it just takes a bit more time and attention.
For users on the Complete monthly plan, the first report is entered free of charge, and each additional report incurs a fee of $15.
Unlimited account holders enjoy the entry of ten reports without charge. Subsequent reports are subject to a $15 fee per report.
Additionally, users on the Complete plan can upgrade to a yearly subscription from the account settings. The annual subscription includes a data entry service for five reports.
All professional accounts allow you to import and onboard an unlimited number of clients and their lab results. The distinction between professional plans lies solely in the data entry service.
The Pro Monthly Plus plan is priced at $75 per month and includes a data entry service for five reports each month. Additional reports can be self-entered at no extra cost or, if preferred, you can use our data entry service for an additional fee of $15 per report.
The Pro Monthly plan is priced at $45 per month and does not include a data entry service. Self-entry is free for an unlimited number of reports, and you can opt for the data entry service at a fee of $15 per report.
You also have the option to upgrade to higher monthly or to annual plans, which come with substantial discounts. All upgrades can be done directly from your account.
Simply log in and navigate to your account settings to cancel your subscription. Scroll down to locate the 'Cancel' button at the bottom of the page. Ensure you cancel at least one day before the renewal date to prevent any charges. Once cancellation is requested, the subscription remains active until the conclusion of the current billing cycle.
Our goal has been to make your Healthmatters account as intuitive as possible.
We've crafted multiple ways for you to navigate your data, whether you're glancing at a single report or delving into your historical test reports.
1. Graph View:Dive into a visual journey with our biomarker graphs, showcasing over 40 data points. Combining years of results unveils trends, empowering you to make informed decisions. Our visualization tools make it a breeze to compare and understand changes over time, even if your results are from different labs. A search function and filters simplify the exploration of extensive data, allowing you to focus on what needs attention.
2. All Tests ViewExplore neatly organized reports on a timeline, highlighting crucial details like dates, critical results, and lab/panel names. Each report opens up to reveal in-depth descriptions and additional recommendations for each biomarker. The history of previous results is just a click away, and you can download a comprehensive report for deeper insights. Color-coded and user-friendly, it's designed for easy reading, understanding, and navigation.
3. Table View:For a holistic view of all biomarkers side by side, our table view is your go-to. Results are neatly displayed in a categorized and dated table, ideal for those with an extensive test history. Utilize sorting, filters, and color-coding to enhance your analysis and gain extra insights.
Yes, you can download your information anytime. We offer two easy ways to export your lab data:
This makes it simple to save, back up, or share your health data whenever you need.
Yes, you can print your report. To do so, navigate to "All tests" and open the report you wish to print. You'll find a print button in the right corner of the report. Click on it, and your browser's print window will open. If you prefer to print in a bigger typeface, adjust the scale using the print window settings.
Yes, you can! We highly recommend activating Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for your account. To do so, please navigate to the "Profile and Security" section of your account, where you will find instructions for activating 2FA.
Yes, you can. When entering values for the biomarker, you will see an "Edit Range" button. Click this button, and you'll have the option to enter a custom range.
A personal account is all about keeping your own lab test results in check. It's just for you and your personal use.
The professional account is designed for health professionals who wish to track and organize their clients' laboratory results.
To learn more about Healthmatters Pro, please refer to the professional page.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.

