Aflatoxins were initially isolated and identified as the causative toxins in Turkey X disease (necrosis of the liver) in 1960 when over 100,000 turkeys died in England (Asao, 1963). They are the most studied mycotoxins with over 5,000 research papers published through 2002. There are four generally recognized Aflatoxins designated B1, B2, G1 and G2 . The metabolites, M1 & M2, are found in milk (Thirumala-Devi et al (2002).
The order of toxicity is B1 greater than G1, greater than G2, greater than B2. (IARC, 1976). However, Aflatoxin B1 is the major mycotoxin produced by most species under culture conditions (Ciegler & Bennet, 1980). Because of this and its toxicity, B1 is the most frequently studied of the four.
Aflatoxins are produced by different species of Aspergillus, particularly flavus, oryzae, fumigatus and parasiticus, as well as members of the genera Penicillium (El-Naghy et al, 1991; Searle 1976; Aflatoxins 2002). Strains of Aspergillus flavus and parasiticus produce mycotoxins under favorable conditions.
Aflatoxins can contaminate corn, cereals, sorghum, peanuts and other oil-seed crops. Thus, food contamination by this group of mycotoxins has been implicated in both animal and human Aflatoxicosis.
Aflatoxins are carcinogenic to humans and animals. Overall summary evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans is Group 1 (IARC, 1976; Searle, 1976; Dominguez-Malagon & Gaytan-Graham (2001).
Aflatoxin B1 is a potent liver carcinogen in a variety of experimental animals. It causes liver tumors in mice, rats, fish, marmosets, tree shrews and monkeys following administration by various routes. Types of cancers described in research animals include hepatocellular carcinoma (rats), colon and kidney (rats), cholangiocellular cancer (hamsters), lung adenomas (mice), and osteogenic sarcoma, adenocarcinoma of the gall bladder and carcinoma of the pancreas (monkeys) (IARC, 1976).
In humans, Aflatoxin B1 has been linked to hepatocellular carcinoma from three studies reported in the medical literature, as follows:
An increased incidence (10 % excess) of hepatocellular carcinoma was reported in the southeastern portion of the U.S. in areas of high daily intake of Aflatoxin B1. The daily intake of B1 in the southeastern subjects was 13-197 ug/kg body weight as compared to those in northern and western areas with a daily intake of 0.2-0.3 ug/kg body weight (IARC, 1987).
In China, a strong correlation between the intake of peanut, peanut oil and corn and increased mortality rates for liver cancer were reported in five groups of inhabitants from four villages. The mortality rates were 125, 97.40, 41.65, 24.01 and 1.05, respectively. The median intake of aflatoxin B1 for each group was 6.05, 6.36, 2.69, 1.83 and 0 ug/day. The median daily urine concentrations of M1 metabolite were 16.46, 8, 29, 4.78 and 1.21 ng/person. A significant correlation was found between the mortality rates of primary liver cancer and intake of aflatoxin B1. Further, analysis of M1 in the urine can be used as an index for human exposure to aflatoxin B1 in an epidemiological study (Aflatoxins, 2002).
Cancer in 67 men who had inhaled particles contaminated with aflatoxin were reported in an 11-year follow up study. They worked in a mill crushing peanuts and other oil seeds. Two of the men developed fatal liver disease, while eleven developed cancers of various organs. The 13 men had inhaled doses estimated to be between 160 to 395 ug/cubic meter/man/wk. In 55 matched control men, 4 developed cancer and none died from liver disease. The excess cancers in this study was not significant, however the number of subjects was insufficient to exclude a significant positive correlation (Aflatoxins, 2002; IARC,1976).
Finally, it was reported that in hepatocellular carcinoma cases exposed to aflatoxin B1, mutation of p53 gene is fixed at codon 249 third base and takes the form of G to T transversion. It appears from the reported observations that it is a definite marker of mutation, which is induced by aflatoxin B1 mutagen and is applicable for molecular epidemiology survey of sufferers of aflatoxin B1 exposure among hepatocellular carcinoma cases (Deng & Ma, 1998).
Aflatoxins are among the most toxic and carcinogenic substances found in the environment. These mycotoxins are primarily produced by Aspergillus species and commonly contaminate a variety of food products, including beans, corn, rice, tree nuts, wheat, milk, eggs, and meat. They can even be detected in human tissues, particularly in cases of lung aspergilloma.
Susceptibility to aflatoxin toxicity depends on multiple factors, including age, sex, diet, and genetic makeup. Aflatoxins are known to cause:
Liver damage and hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
Mental impairment, abdominal pain, hemorrhaging, coma, and death in severe cases
Encephalopathy and Reye’s syndrome, particularly in children
Immunotoxicity, including reduced leukocyte proliferation and elevated alpha tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) levels
Birth and neonatal risks, such as developmental toxicity, increased susceptibility to infections, jaundice, and poor vaccine response
Clinical signs of aflatoxicosis may include:
Non-itchy macular rash
Headache and gastrointestinal distress
Lower limb edema
Anemia and jaundice
Aflatoxins have been found in:
Human cord blood and breast milk
Cow’s milk, dairy products, and infant formula
Tissues of both humans and animals, indicating widespread food chain contamination
Animal studies have confirmed immunosuppressive effects across multiple species, and exposure during gestation may impact fetal development.
Aflatoxin B1 has been shown to induce mutations in both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. Individuals with specific genetic polymorphisms—such as GSTM1 null, mEH heterozygote, or CYP3A5 mutations—may have increased levels of albumin-aflatoxin adducts, indicating higher vulnerability to toxicity.
Supportive care includes hydration to prevent dehydration and manage systemic effects.
Nutritional support: Diets rich in carrots, parsnips, celery, and parsley may reduce aflatoxin’s carcinogenic effects.
Clay binders like bentonite may reduce intestinal absorption of aflatoxins from contaminated food.
Supplementation with chlorophyllin, zinc, and vitamins A, C, and E has shown potential in reducing toxicity.
Pharmacologic support: Oltipraz enhances detoxification by promoting glutathione conjugation and inhibiting harmful P450-mediated metabolism.
Aflatoxin toxicity can be exacerbated by co-exposure to other mycotoxins such as ochratoxin and zearalenone, highlighting the importance of comprehensive food safety monitoring.
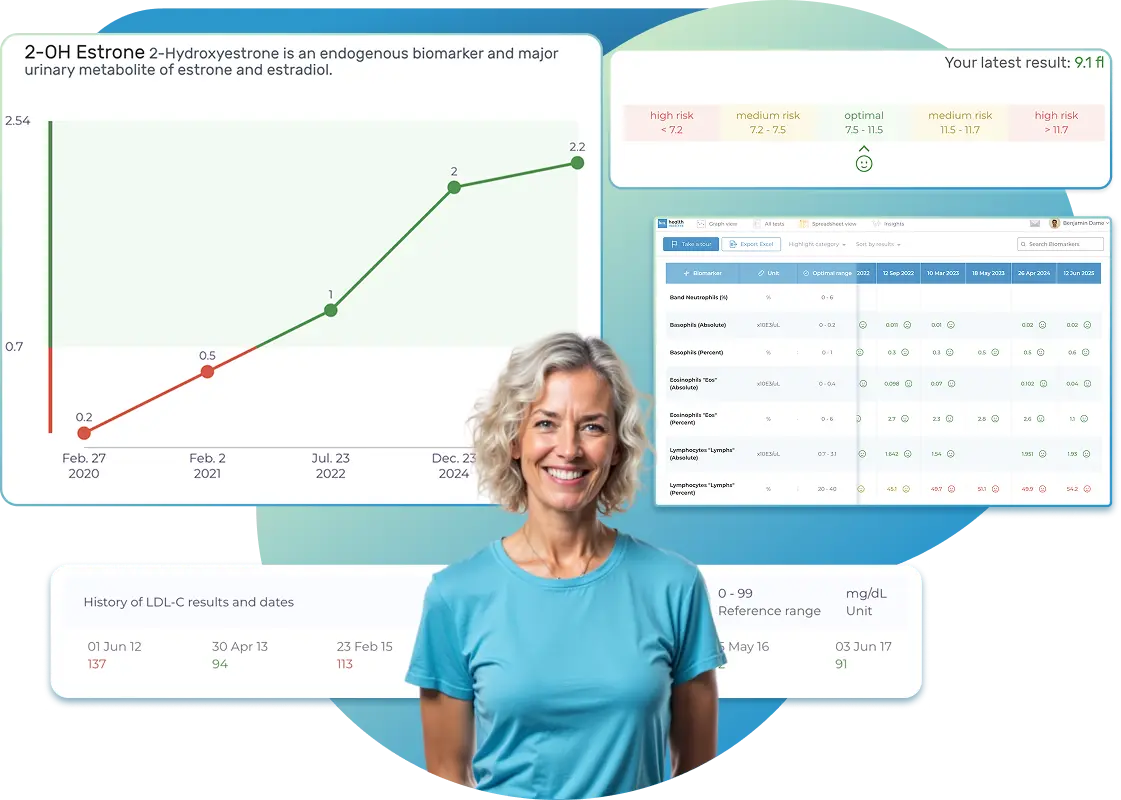
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
Laboratories
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.











Pricing Table
Choose the plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clear insights you can finally use.
Pick a plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clarity.
Personal plans
Professional plan
$15/ month
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
$250/ once
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
Professional plan
$45/ month
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
About membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
Easily upload lab results from any provider, whether it's a hospital, independent lab, or home testing service. We support PDFs, scanned documents, and JPEGs from patient portals. No need to log in to multiple platforms — everything is centralized in one secure space.
Easily upload lab results from any provider — we support PDFs, scans, and images. Keep all your reports organized in one secure place.
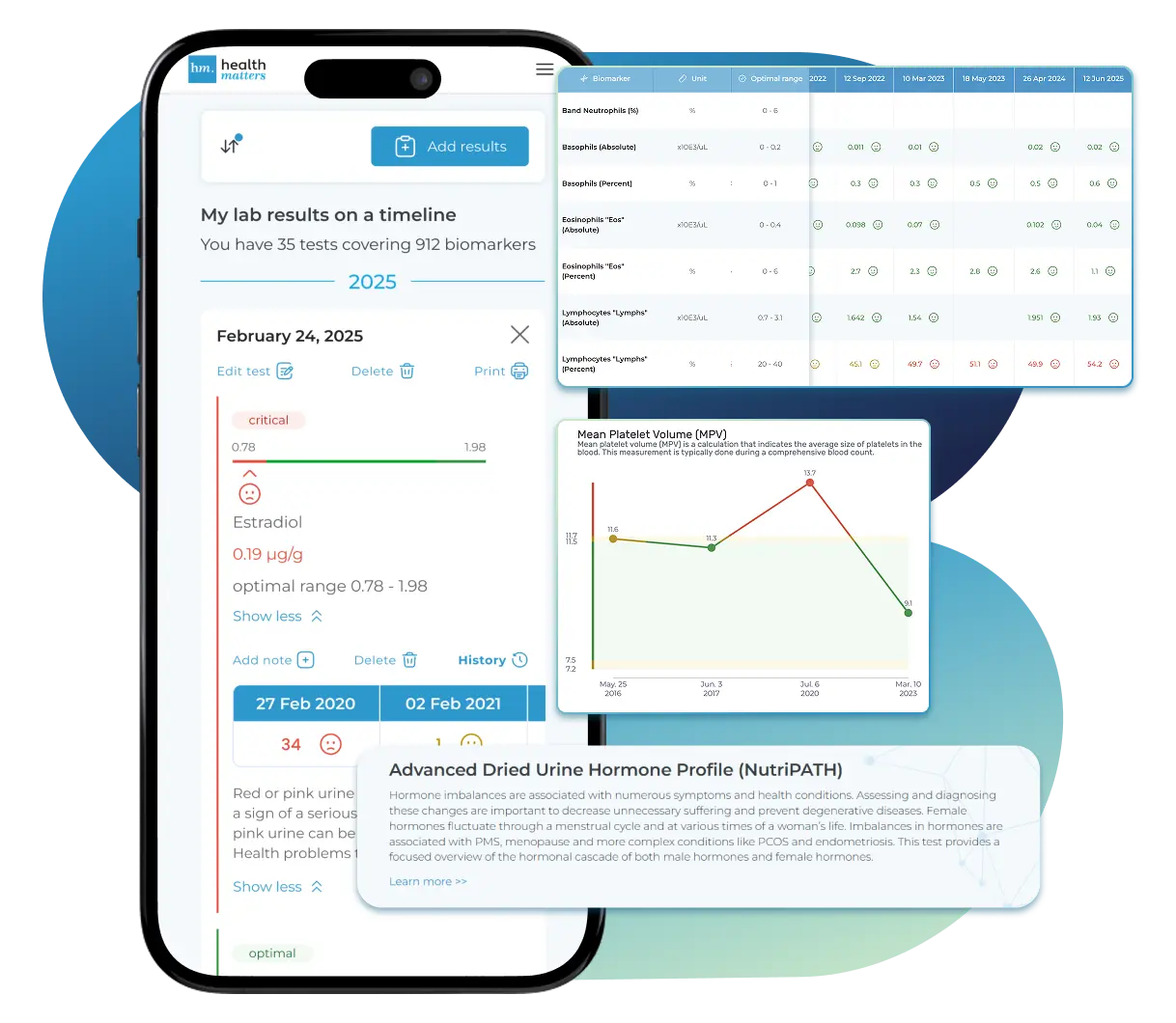
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey. Whether you're tracking a condition, managing treatments, or staying proactive, the timeline helps you and your doctor understand how things progress over time.
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey.
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
Whether it's a blood test, GI panel, urinalysis, or something else, lab reports measure numerous biomarkers that reveal what's happening inside your body. Our extensive database covers over 10,000 biomarkers, providing clear, simple explanations of what each result means and how you can take action—no matter your membership level. Say goodbye to confusion and get the insights you need to better understand your health.
Our database covers over 10,000 biomarkers with clear, simple explanations—so you can finally understand your results and what to do next.
 Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
If you'd like to handle inputting your health data into your account, you can do so with our easy-to-use data entry forms. Our user-friendly form is designed to guide you through the quick and easy submission process, making it simple to keep track of your health metrics. This is available to both Complete plan and Unlimited plan members.
Our user-friendly form guides you through a quick, simple submission process, making it easy to enter your health metrics.
Add your results anytime with our easy entry form. It's quick, guided, and helps you stay organized — free for all members.
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
View your lab data through easy-to-read graphs and tables. Quickly spot patterns, track changes, and compare results across different dates — all without digging through multiple reports. You can also select and compare graphs of specific biomarkers side-by-side to better understand how they relate and change over time.
See your lab reports in clear graphs and tables. Spot patterns, track changes, and compare results over time — all in one place.
 Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file. Choose from PDF, Excel, or CSV formats to easily review, share, or get a second opinion—no more juggling multiple reports.
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file.
 Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest. Complete plan members receive one report entered for free, then $15 per report after that. Unlimited plan members receive ten report entries for free, then $15 per report after that.
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest.
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Whether you're working with a doctor, nutritionist, caregiver, or wellness coach, you can securely share your complete lab history by sending an invite link to anyone you trust. You have full control over who sees your information and for how long, ensuring your privacy and peace of mind at every step.
Share your full lab history with your doctor, nutritionist, or coach using a secure invite link.
Discover






I have been using Healthmatters.io since 2021. I travel all over the world and use different doctors and health facilities. This site has allowed me to consolidate all my various test results over 14 years in one place. And every doctor that I show this to has been impressed. Because with any health professional I talk to, I can pull up historical results in seconds. It is invaluable. Even going back to the same doctor, they usually do not have the historical results from their facility in a graph format. That has been very helpful.
Anthony
Unlimited Plan Member since 2021

What fantastic service and great, easy-to-follow layouts! I love your website; it makes it so helpful to see patterns in my health data. It's truly a pleasure to use. I only wish the NHS was as organized and quick as Healthmatters.io. You've set a new standard for health tracking!
Karin
Advanced Plan Member since 2020

As a PRO member and medical practitioner, Healthmatters.io has been an invaluable tool for tracking my clients' data. The layout is intuitive, making it easy to monitor trends and spot patterns over time. The ability to customize reports and charts helps me present information clearly to my clients, improving communication and outcomes. It's streamlined my workflow, saving me time and providing insights at a glance. Highly recommended for any practitioner looking for a comprehensive and user-friendly solution to track patient labs!
Paul
Healthmatters Pro Member since 2024
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 4000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
While we work with many popular labs, we welcome reports from lots of other places too.
It's as simple as this: if you can get a test done, you can upload it to Healthmatters and we can interpret results from any lab out there. If laboratories can analyze it, we can interpret it.
If you're on the hunt for a specific biomarker, contact us and we'll add it to our database. Anything from blood, urine, saliva, or stool can be uploaded, understood, and tracked with your Healthmatters account.
The Complete Plan ($15/month) is perfect for individuals who want ongoing access to their health data. It includes unlimited lab imports, visual tracking, custom ranges, result explanations, full account exports, and secure sharing — all with a simple monthly subscription. You can cancel anytime and restart your plan whenever you're ready — your data will still be there waiting for you. You can also upgrade to the Unlimited Plan at any time, with the cost prorated based on what you've already paid.
The Unlimited Plan ($250 one-time) is also designed for individuals but offers lifetime access with no ongoing subscription. You'll get all the same features as the Complete Plan, plus a larger initial data entry allowance (10 reports), making it a great choice if you prefer a one-time payment and long-term use without monthly fees.
In short:
There are two ways to add your test reports to your Healthmatters account. One option is to input the data using the data entry forms. The other method is to utilize our "Data entry service."
Our data entry forms offer an easy, fast, and free way for you to input the reports yourself. Self-entry allows you to add an unlimited number of reports at no cost. We make the self-entry process user-friendly, providing dozens of templates that pre-populate the most popular laboratory panels and offering instant feedback on entered values.
For those who prefer assistance, we offer a "Data entry service" to help you input your data. Simply attach an image or file of your lab test results, and a qualified team member from our data entry team will add the results for you.
We support various file types, including PDFs, JPGs, or Excel. This service is particularly useful if you have many reports to upload or if you're too busy to handle the data entry yourself.
Our Data Entry Service is for when you don't want to manually type in your lab results yourself. You simply upload your report (PDF, image, or screenshot), and our trained team enters the information into your Healthmatters account for you — accurately and neatly organized, ready to view in graphs, tables, and timelines.
The $15 per report covers the time and care it takes for a real person to review your file, make sure each result is entered correctly, and double-check for accuracy. This ensures your health data is precise and easy to work with — without you having to spend the time doing it yourself.
Prefer to do it yourself? You can always use our free self-entry tool to add results manually — it just takes a bit more time and attention.
For users on the Complete monthly plan, the first report is entered free of charge, and each additional report incurs a fee of $15.
Unlimited account holders enjoy the entry of ten reports without charge. Subsequent reports are subject to a $15 fee per report.
Additionally, users on the Complete plan can upgrade to a yearly subscription from the account settings. The annual subscription includes a data entry service for five reports.
All professional accounts allow you to import and onboard an unlimited number of clients and their lab results. The distinction between professional plans lies solely in the data entry service.
The Pro Monthly Plus plan is priced at $75 per month and includes a data entry service for five reports each month. Additional reports can be self-entered at no extra cost or, if preferred, you can use our data entry service for an additional fee of $15 per report.
The Pro Monthly plan is priced at $45 per month and does not include a data entry service. Self-entry is free for an unlimited number of reports, and you can opt for the data entry service at a fee of $15 per report.
You also have the option to upgrade to higher monthly or to annual plans, which come with substantial discounts. All upgrades can be done directly from your account.
Simply log in and navigate to your account settings to cancel your subscription. Scroll down to locate the 'Cancel' button at the bottom of the page. Ensure you cancel at least one day before the renewal date to prevent any charges. Once cancellation is requested, the subscription remains active until the conclusion of the current billing cycle.
Our goal has been to make your Healthmatters account as intuitive as possible.
We've crafted multiple ways for you to navigate your data, whether you're glancing at a single report or delving into your historical test reports.
1. Graph View:Dive into a visual journey with our biomarker graphs, showcasing over 40 data points. Combining years of results unveils trends, empowering you to make informed decisions. Our visualization tools make it a breeze to compare and understand changes over time, even if your results are from different labs. A search function and filters simplify the exploration of extensive data, allowing you to focus on what needs attention.
2. All Tests ViewExplore neatly organized reports on a timeline, highlighting crucial details like dates, critical results, and lab/panel names. Each report opens up to reveal in-depth descriptions and additional recommendations for each biomarker. The history of previous results is just a click away, and you can download a comprehensive report for deeper insights. Color-coded and user-friendly, it's designed for easy reading, understanding, and navigation.
3. Table View:For a holistic view of all biomarkers side by side, our table view is your go-to. Results are neatly displayed in a categorized and dated table, ideal for those with an extensive test history. Utilize sorting, filters, and color-coding to enhance your analysis and gain extra insights.
Yes, you can download your information anytime. We offer two easy ways to export your lab data:
This makes it simple to save, back up, or share your health data whenever you need.
Yes, you can print your report. To do so, navigate to "All tests" and open the report you wish to print. You'll find a print button in the right corner of the report. Click on it, and your browser's print window will open. If you prefer to print in a bigger typeface, adjust the scale using the print window settings.
Yes, you can! We highly recommend activating Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for your account. To do so, please navigate to the "Profile and Security" section of your account, where you will find instructions for activating 2FA.
Yes, you can. When entering values for the biomarker, you will see an "Edit Range" button. Click this button, and you'll have the option to enter a custom range.
A personal account is all about keeping your own lab test results in check. It's just for you and your personal use.
The professional account is designed for health professionals who wish to track and organize their clients' laboratory results.
To learn more about Healthmatters Pro, please refer to the professional page.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.

