Other names: Triiodothyronine (T3, total), T3(THYRONINE), TOTAL, Triiodothyronine (T3)
The T3 test measures triiodothyronine in blood to help doctors diagnose hyperthyroidism. The total triiodothyronine (T3) test is one of several tests used to diagnose thyroid disorders. T3 is an active thyroid hormone that your body creates by converting thyroxine (T4) into triiodothyronine. The 3 and 4 in the names represent the number of iodine atoms it has.
T3 helps maintain muscle control, brain function and development, heart and digestive functions. High or low T3 levels may indicate an overactive or underactive thyroid.
What is the Thyroid?
The thyroid gland is located in front of your neck. It has right and left lobes that resemble a butterfly. This gland produces hormones that help control your metabolism, which is how your body uses energy. Disorders that affect thyroid function can either speed up or slow down metabolic processes.
Thyroid problems can cause a wide range of symptoms and affect your:
→ Appetite and weight
→ Body temperature
→ Energy level
→ Heart rate (Hyperthyroidism causes a fast heartbeat)
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
If you have symptoms that might point to thyroid problems, this test helps your doctor identify the cause.
What Is T3?
T3 (triiodothyronine) is a hormone that helps control many body functions, including growth, body temperature, and heart rate. When your thyroid gland is working properly, it makes and releases a hormone called thyroxine, or T4. Your blood carries T4 around your body where your liver, brain, and other tissues turn some of it into triiodothyronine, or T3.
There are two types of T3 in your blood:
→ Bound T3, which attaches to proteins that help carry the hormone through the body.
→ Free T3, which is not attached to proteins.
The Total T3 test measures levels of both the bound and free types of T3.
More about the T3 test:
The T3 test can also help your doctor identify thyroid cancer and other uncommon conditions that can affect your thyroid.
T3 tests are often useful to diagnose hyperthyroidism or to determine the severity of the hyperthyroidism. Patients who are hyperthyroid will have an elevated T3 level. In some individuals with a low TSH, only the T3 is elevated and the FT4 or FTI is normal.
T3 testing rarely is helpful in the hypothyroid patient, since it is the last test to become abnormal. Patients can be severely hypothyroid with a high TSH and low FT4 or FTI, but have a normal T3.
Doctors order T3 total tests when they’re checking a person’s thyroid function. Doctors may order the T3 test when a child's symptoms or previous blood tests suggest a thyroid problem. The T3 test is particularly useful in diagnosing hyperthyroidism. In this condition, the thyroid overproduces hormones, causing symptoms such as a fast heart rate, weight loss, trembling, and sweating.
The T3 test simply measures how much of this hormone is present in your blood. If the level is either abnormally high or abnormally low, it can be an indicator of thyroid disease. However, this test is generally more useful for diagnosing hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) than hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), and it's typically combined with measures of other thyroid hormone levels rather than taken alone.
Total T3 tests are generally ordered when you have symptoms that are consistent with thyroid disease, especially if you have an elevated risk. Risk factors include being female, being under the age of 40, and having family members who are diagnosed with thyroid disorders.
Your healthcare provider will likely order other measurements of thyroid function at the same time as T3 test including tests of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4. Tests to look for antibodies that indicate autoimmune thyroid disease, including Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease.
The T3 test, as well as other thyroid tests, are performed on blood samples. The process for drawing blood for these tests is generally quick, simple, and low-risk.
What do normal, high, and low levels mean?
Normal T3 levels in the blood range from 71 - 180 ng/dL (nanograms per deciliter).
If your levels are higher than normal, that could mean you have an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an uncommon condition such as thyroid cancer.
If your levels are lower than normal, that could be a sign of an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or chronic illness. Your doctor will need to order other tests in order to diagnose these issues.
Why is the Free T3 blood test better than the Total T3 blood test?
Measuring total T3 (both bound and unbound) may give misleading information if the binding proteins are increased or decreased
Therefore, most healthcare providers today rely on the free T3 blood test instead of the total T3 blood test.
In more than 70% of cases, hyperthyroidism is due to Graves’ disease, which occurs most often in females and can run in families. Nodules and lumps that grow on the thyroid can also cause hyperthyroidism. Doctors refer to this as toxic nodular goiter.
How to interpret Thyroid test results?
The table below provides examples of test results and their possible interpretation:
| TSH | FREE T4 | FREE OR TOTAL T3 | THYROID FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal thyroid function |
| High | Normal | Normal | Subclinical hypothyroidism |
| High | Low | Normal or low | Primary hypothyroidism related to the thyroid gland |
| Low or undetectable | Normal | Normal | Subclinical hyperthyroidism |
| Low | High | High | Primary hyperthyroidism related to the thyroid gland |
| Low | Low | Low or normal | Secondary hypothyroidism related to the pituitary gland |
| Normal or high | High | High | Secondary hyperthyroidism related to pituitary gland |
Subclinical hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are conditions defined by abnormal TSH test results with normal T3 and T4 levels. These subclinical conditions often cause no symptoms or only very mild ones. Some subclinical thyroid conditions may progress to outright hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism over time.
References:
American Thyroid Association, Thyroid Function Tests; https://www.thyroid.org/thyroid-function-tests
Lab Tests Online, American Association for Clinical Chemistry; T3 (Free and Total); https://labtestsonline.org/tests/t3-free-and-total
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Thyroid Tests; https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diagnostic-tests/thyroid
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Free T4 Test - https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003517.htm
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Hyperthyroidism - https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000356.htm
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. T3 Test - https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003687.htm
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. TSH Test - https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003684.htm
An abnormally high level of T3 isn't generally a sign of thyroid disease by itself, but it is considered along with TSH and T4 levels.
A high T3 level may indicate:
→ Hyperthyroidism if accompanied by a low TSH level
→ Graves' disease if accompanied by a low TSH level and positive tests to detect certain antibodies
→ Toxic nodular goiter (an enlarged thyroid gland that contains a small rounded mass or masses called nodules, which produce too much thyroid hormone.)
→ Liver disease
→ A rare condition called T3 thyrotoxicosis [a clinical state of inappropriately high levels of circulating thyroid hormones (T3 and/or T4) in the body from any cause. It is often incorrectly used interchangeably with hyperthyroidism, which is a form of thyrotoxicosis caused by excessive endogenous thyroid hormone production.]
→ High T3 can also be due to pregnancy or the use of medications containing estrogen.
An abnormally low T3 level may indicate:
→ Hypothyroidism, if accompanied by a high TSH level
→ Hashimoto's thyroiditis, if accompanied by a high TSH level and positive tests to detect certain antibodies
→ Malnutrition/starvation
→ A severe short-term illness or some long-term illnesses
Keep in mind that this test has some limitations, which are that:
→ T3 is largely bound to blood proteins (99.7%)
→ Only unbound T3 is active
How to interpret Total T3 together with TSH?
What is TSH?
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland in the brain. Its primary role is to regulate the thyroid gland's activity by stimulating the production and release of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). TSH levels in the bloodstream rise when thyroid hormone levels are too low, signaling the thyroid gland to increase hormone production. Conversely, when thyroid hormone levels are too high, TSH levels decrease to reduce thyroid hormone production. TSH is a crucial marker used in assessing thyroid function, with abnormal levels indicating potential thyroid disorders, such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
How to interpret those markers together:
Interpreting Total T3 (triiodothyronine) levels together with Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels can provide valuable insights into a person's thyroid function. TSH is often considered the most sensitive marker for thyroid function, while Total T3 provides information about the actual thyroid hormone levels in the bloodstream. Here's how to interpret these two tests together:
Normal Thyroid Function:
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid):
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid):
Secondary or Tertiary Hypothyroidism:
It's important to note that Total T3 measures the total amount of T3 in the bloodstream, including both free (biologically active) and bound T3. While it can provide valuable information, some healthcare providers prefer to use Free T3 levels for a more accurate assessment of thyroid function, as discussed in a previous section above.
How to treat elevated Total T3 levels?
Elevated Total T3 (triiodothyronine) levels can be a sign of hyperthyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces an excess of thyroid hormones, including T3. Treatment for elevated Total T3 levels typically involves addressing the underlying cause, which is often an overactive thyroid. Here are common treatment approaches:
Anti-Thyroid Medications:
In cases of hyperthyroidism, healthcare providers may prescribe anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU). These drugs help reduce the production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy:
Radioactive iodine therapy involves the administration of a radioactive substance that selectively destroys thyroid cells, reducing hormone production. This treatment is often used when antithyroid medications are ineffective or not well-tolerated.
Beta-Blockers:
Beta-blockers like propranolol may be prescribed to manage symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety. Beta-blockers do not treat the underlying thyroid condition but can provide relief from certain symptoms.
Surgery (Thyroidectomy):
In some cases, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be recommended, especially when medications and radioactive iodine therapy are not suitable or effective.
Monitoring:
Regular monitoring of thyroid function through blood tests, including Total T3 and other thyroid markers, is crucial to assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust medication doses as needed.
The specific treatment approach depends on the underlying cause of the elevated Total T3 levels, the severity of hyperthyroidism, and individual patient factors. It's essential to work closely with a healthcare provider or an endocrinologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet, managing stress, and getting enough rest, can complement medical treatment and help support thyroid health. It's essential to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations and attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure that your thyroid function returns to a healthy balance.
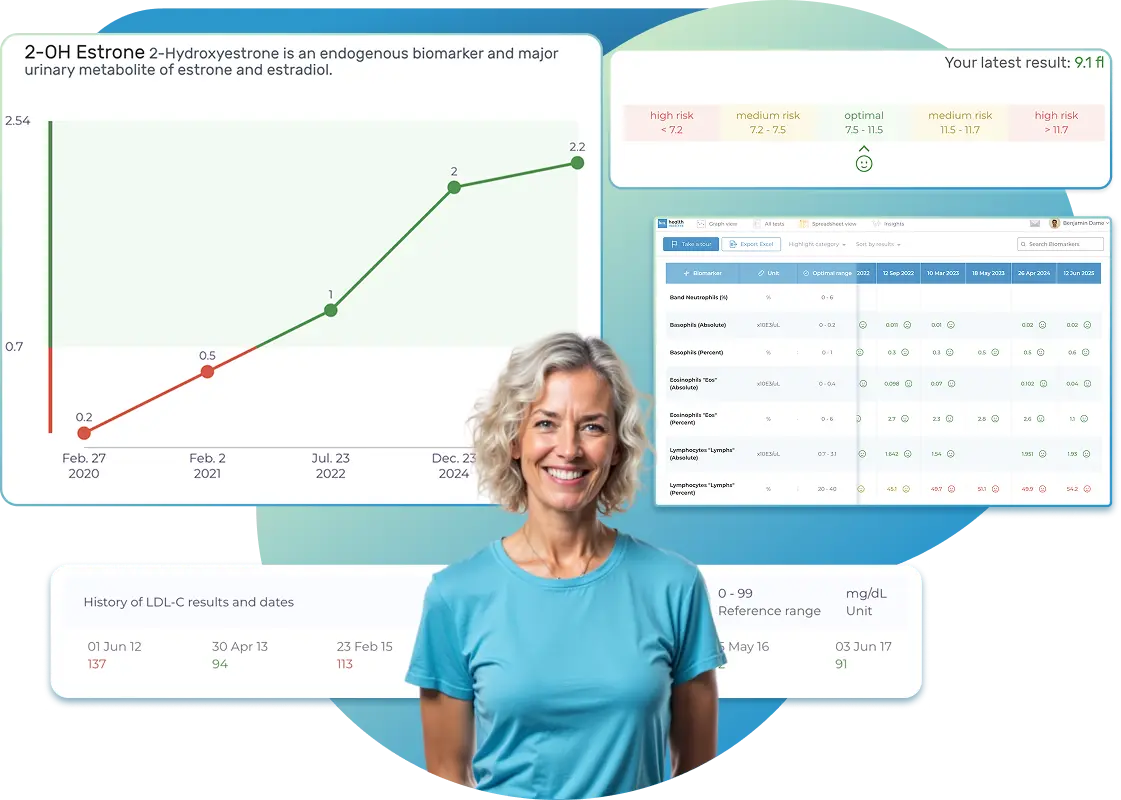
Import lab results from multiple providers, track changes over time, customize your reference ranges, and get clear explanations for each result. Everything is stored securely, exportable in one organized file, and shareable with your doctor—or anyone you choose.
Cancel or upgrade anytime
Low Total T3 (triiodothyronine) levels typically indicate a deficiency in thyroid hormone production or conversion, a condition known as hypothyroidism.
This can result from various underlying causes, including:
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis,
- iodine deficiency,
- certain medications,
- or pituitary gland dysfunction.
Hypothyroidism can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- fatigue,
- weight gain,
- cold intolerance,
- dry skin,
- and cognitive impairment.
Treatment for low Total T3 levels involves hormone replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormones, primarily levothyroxine (T4).
The goal is to restore thyroid hormone levels to the normal range, as T4 can be converted into the active T3 in the body as needed. The dosage of levothyroxine is adjusted based on regular blood tests, including TSH, Free T4, and Free T3, to ensure thyroid hormone levels are optimized and symptoms are relieved. It's crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and monitor thyroid function regularly to achieve and maintain a healthy thyroid balance.
Some lifestyle and dietary practices may complement medical treatment and support thyroid health:
Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in nutrients, including iodine and selenium, which are essential for thyroid function. Good sources of iodine include seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt. Selenium-rich foods include Brazil nuts, fish, and whole grains.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can impact thyroid function. Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or relaxation techniques to reduce stress levels.
Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help support overall health and metabolism, which can indirectly benefit thyroid function.
Get Adequate Sleep: Prioritize good sleep hygiene and aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support overall well-being, including thyroid health.
Avoid Goitrogenic Foods: Some foods contain compounds known as goitrogens that can interfere with thyroid function. These include raw cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower), soy products, and millet. Cooking these foods can help reduce their goitrogenic effects.
Limit Processed Foods: Minimize your intake of processed and sugary foods, as they can contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances that may affect thyroid function.
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for overall health and can help support metabolic processes.
Important note:
While these lifestyle and dietary practices can promote overall well-being and may have a positive impact on thyroid health, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your thyroid function or low Total T3 levels. Natural methods alone may not be sufficient to address thyroid disorders, and medical evaluation and treatment are often necessary to restore thyroid hormone balance. Always follow your healthcare provider's guidance and treatment recommendations for thyroid-related conditions.
Laboratories
We accept reports from any lab, so you can easily collect and organize all your health information in one secure spot.











Pricing Table
Choose the plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clear insights you can finally use.
Pick a plan that fits you — and turn scattered lab reports into clarity.
Personal plans
Professional plan
$15/ month
Access your lab reports, explanations, and tracking tools.
$250/ once
Pay once, access everything—no monthly fees, no limits.
Professional plan
$45/ month
Designed for professionals managing their clients' lab reports
About membership
 Import Lab Results from Any Source
Import Lab Results from Any Source
Easily upload lab results from any provider, whether it's a hospital, independent lab, or home testing service. We support PDFs, scanned documents, and JPEGs from patient portals. No need to log in to multiple platforms — everything is centralized in one secure space.
Easily upload lab results from any provider — we support PDFs, scans, and images. Keep all your reports organized in one secure place.
 See Your Health Timeline
See Your Health Timeline
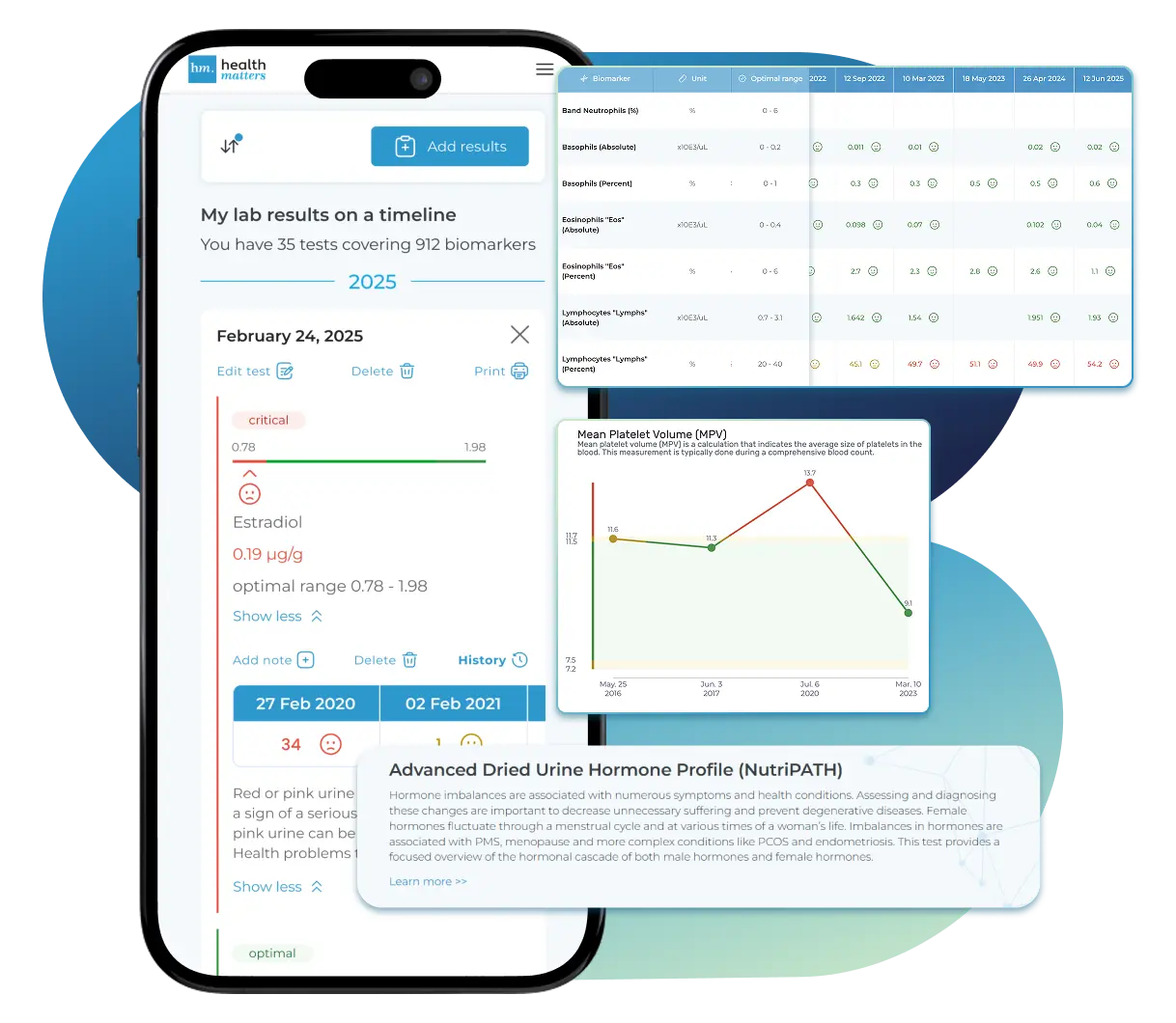
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey. Whether you're tracking a condition, managing treatments, or staying proactive, the timeline helps you and your doctor understand how things progress over time.
Every lab result is automatically organized on a chronological timeline, giving you a complete picture of your health journey.
 Understand What Your Results Mean
Understand What Your Results Mean
Whether it's a blood test, GI panel, urinalysis, or something else, lab reports measure numerous biomarkers that reveal what's happening inside your body. Our extensive database covers over 10,000 biomarkers, providing clear, simple explanations of what each result means and how you can take action—no matter your membership level. Say goodbye to confusion and get the insights you need to better understand your health.
Our database covers over 10,000 biomarkers with clear, simple explanations—so you can finally understand your results and what to do next.
 Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports Yourself — Always Free
Enter Your Lab Reports — Always Free
If you'd like to handle inputting your health data into your account, you can do so with our easy-to-use data entry forms. Our user-friendly form is designed to guide you through the quick and easy submission process, making it simple to keep track of your health metrics. This is available to both Complete plan and Unlimited plan members.
Our user-friendly form guides you through a quick, simple submission process, making it easy to enter your health metrics.
Add your results anytime with our easy entry form. It's quick, guided, and helps you stay organized — free for all members.
 Visualize Your Results
Visualize Your Results
View your lab data through easy-to-read graphs and tables. Quickly spot patterns, track changes, and compare results across different dates — all without digging through multiple reports. You can also select and compare graphs of specific biomarkers side-by-side to better understand how they relate and change over time.
See your lab reports in clear graphs and tables. Spot patterns, track changes, and compare results over time — all in one place.
 Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
Export Your Complete Lab History in a Single File
Export Your Complete Lab History
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file. Choose from PDF, Excel, or CSV formats to easily review, share, or get a second opinion—no more juggling multiple reports.
After collecting lab results from different providers, you can download your entire history combined into a single file.
 Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Comprehensive Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Data Entry Service for Your Reports
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest. Complete plan members receive one report entered for free, then $15 per report after that. Unlimited plan members receive ten report entries for free, then $15 per report after that.
Our inclusive service handles the data entry for your lab reports. Just submit your information and we'll take care of the rest.
 Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Securely Share With Anyone You Trust
Whether you're working with a doctor, nutritionist, caregiver, or wellness coach, you can securely share your complete lab history by sending an invite link to anyone you trust. You have full control over who sees your information and for how long, ensuring your privacy and peace of mind at every step.
Share your full lab history with your doctor, nutritionist, or coach using a secure invite link.
Discover






I have been using Healthmatters.io since 2021. I travel all over the world and use different doctors and health facilities. This site has allowed me to consolidate all my various test results over 14 years in one place. And every doctor that I show this to has been impressed. Because with any health professional I talk to, I can pull up historical results in seconds. It is invaluable. Even going back to the same doctor, they usually do not have the historical results from their facility in a graph format. That has been very helpful.
Anthony
Unlimited Plan Member since 2021

What fantastic service and great, easy-to-follow layouts! I love your website; it makes it so helpful to see patterns in my health data. It's truly a pleasure to use. I only wish the NHS was as organized and quick as Healthmatters.io. You've set a new standard for health tracking!
Karin
Advanced Plan Member since 2020

As a PRO member and medical practitioner, Healthmatters.io has been an invaluable tool for tracking my clients' data. The layout is intuitive, making it easy to monitor trends and spot patterns over time. The ability to customize reports and charts helps me present information clearly to my clients, improving communication and outcomes. It's streamlined my workflow, saving me time and providing insights at a glance. Highly recommended for any practitioner looking for a comprehensive and user-friendly solution to track patient labs!
Paul
Healthmatters Pro Member since 2024
Healthmatters is a personal health dashboard that helps you organize and understand your lab results. It collects and displays your medical test data from any lab in one secure, easy-to-use platform.
With a Healthmatters account, you can:
Professionals can also analyze client data more efficiently and save time managing lab reports.
Healthmatters.io personal account provides in-depth research on 4000+ biomarkers, including information and suggestions for test panels such as, but not limited to:
You can combine all test reports inside your Healthmatters account and keep them in one place. It gives you an excellent overview of all your health data. Once you retest, you can add new results and compare them.
If you are still determining whether Healthmatters support your lab results, the rule is that if you can test it, you can upload it to Healthmatters.
While we work with many popular labs, we welcome reports from lots of other places too.
It's as simple as this: if you can get a test done, you can upload it to Healthmatters and we can interpret results from any lab out there. If laboratories can analyze it, we can interpret it.
If you're on the hunt for a specific biomarker, contact us and we'll add it to our database. Anything from blood, urine, saliva, or stool can be uploaded, understood, and tracked with your Healthmatters account.
The Complete Plan ($15/month) is perfect for individuals who want ongoing access to their health data. It includes unlimited lab imports, visual tracking, custom ranges, result explanations, full account exports, and secure sharing — all with a simple monthly subscription. You can cancel anytime and restart your plan whenever you're ready — your data will still be there waiting for you. You can also upgrade to the Unlimited Plan at any time, with the cost prorated based on what you've already paid.
The Unlimited Plan ($250 one-time) is also designed for individuals but offers lifetime access with no ongoing subscription. You'll get all the same features as the Complete Plan, plus a larger initial data entry allowance (10 reports), making it a great choice if you prefer a one-time payment and long-term use without monthly fees.
In short:
There are two ways to add your test reports to your Healthmatters account. One option is to input the data using the data entry forms. The other method is to utilize our "Data entry service."
Our data entry forms offer an easy, fast, and free way for you to input the reports yourself. Self-entry allows you to add an unlimited number of reports at no cost. We make the self-entry process user-friendly, providing dozens of templates that pre-populate the most popular laboratory panels and offering instant feedback on entered values.
For those who prefer assistance, we offer a "Data entry service" to help you input your data. Simply attach an image or file of your lab test results, and a qualified team member from our data entry team will add the results for you.
We support various file types, including PDFs, JPGs, or Excel. This service is particularly useful if you have many reports to upload or if you're too busy to handle the data entry yourself.
Our Data Entry Service is for when you don't want to manually type in your lab results yourself. You simply upload your report (PDF, image, or screenshot), and our trained team enters the information into your Healthmatters account for you — accurately and neatly organized, ready to view in graphs, tables, and timelines.
The $15 per report covers the time and care it takes for a real person to review your file, make sure each result is entered correctly, and double-check for accuracy. This ensures your health data is precise and easy to work with — without you having to spend the time doing it yourself.
Prefer to do it yourself? You can always use our free self-entry tool to add results manually — it just takes a bit more time and attention.
For users on the Complete monthly plan, the first report is entered free of charge, and each additional report incurs a fee of $15.
Unlimited account holders enjoy the entry of ten reports without charge. Subsequent reports are subject to a $15 fee per report.
Additionally, users on the Complete plan can upgrade to a yearly subscription from the account settings. The annual subscription includes a data entry service for five reports.
All professional accounts allow you to import and onboard an unlimited number of clients and their lab results. The distinction between professional plans lies solely in the data entry service.
The Pro Monthly Plus plan is priced at $75 per month and includes a data entry service for five reports each month. Additional reports can be self-entered at no extra cost or, if preferred, you can use our data entry service for an additional fee of $15 per report.
The Pro Monthly plan is priced at $45 per month and does not include a data entry service. Self-entry is free for an unlimited number of reports, and you can opt for the data entry service at a fee of $15 per report.
You also have the option to upgrade to higher monthly or to annual plans, which come with substantial discounts. All upgrades can be done directly from your account.
Simply log in and navigate to your account settings to cancel your subscription. Scroll down to locate the 'Cancel' button at the bottom of the page. Ensure you cancel at least one day before the renewal date to prevent any charges. Once cancellation is requested, the subscription remains active until the conclusion of the current billing cycle.
Our goal has been to make your Healthmatters account as intuitive as possible.
We've crafted multiple ways for you to navigate your data, whether you're glancing at a single report or delving into your historical test reports.
1. Graph View:Dive into a visual journey with our biomarker graphs, showcasing over 40 data points. Combining years of results unveils trends, empowering you to make informed decisions. Our visualization tools make it a breeze to compare and understand changes over time, even if your results are from different labs. A search function and filters simplify the exploration of extensive data, allowing you to focus on what needs attention.
2. All Tests ViewExplore neatly organized reports on a timeline, highlighting crucial details like dates, critical results, and lab/panel names. Each report opens up to reveal in-depth descriptions and additional recommendations for each biomarker. The history of previous results is just a click away, and you can download a comprehensive report for deeper insights. Color-coded and user-friendly, it's designed for easy reading, understanding, and navigation.
3. Table View:For a holistic view of all biomarkers side by side, our table view is your go-to. Results are neatly displayed in a categorized and dated table, ideal for those with an extensive test history. Utilize sorting, filters, and color-coding to enhance your analysis and gain extra insights.
Yes, you can download your information anytime. We offer two easy ways to export your lab data:
This makes it simple to save, back up, or share your health data whenever you need.
Yes, you can print your report. To do so, navigate to "All tests" and open the report you wish to print. You'll find a print button in the right corner of the report. Click on it, and your browser's print window will open. If you prefer to print in a bigger typeface, adjust the scale using the print window settings.
Yes, you can! We highly recommend activating Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for your account. To do so, please navigate to the "Profile and Security" section of your account, where you will find instructions for activating 2FA.
Yes, you can. When entering values for the biomarker, you will see an "Edit Range" button. Click this button, and you'll have the option to enter a custom range.
A personal account is all about keeping your own lab test results in check. It's just for you and your personal use.
The professional account is designed for health professionals who wish to track and organize their clients' laboratory results.
To learn more about Healthmatters Pro, please refer to the professional page.
At HealthMatters, we're committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. We've put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.

